home → Composition Techniques → Asymmetrical balance
Asymmetrical composition definition
What is asymmetrical balance?
Filmmakers often try to compose shots that achieve a sense of balance. While symmetrical balance would have two sides of a picture mirror each other, asymmetry creates frames where the subjects are off-center. This can still feel balanced, and can often be visually very interesting for viewers. Filmmakers use different techniques - like lighting, color, and blocking - to create asymmetrical shots.
For an in-depth exploration of this technique, check out our full guide to asymmetrical balance, complete with examples and breakdowns.
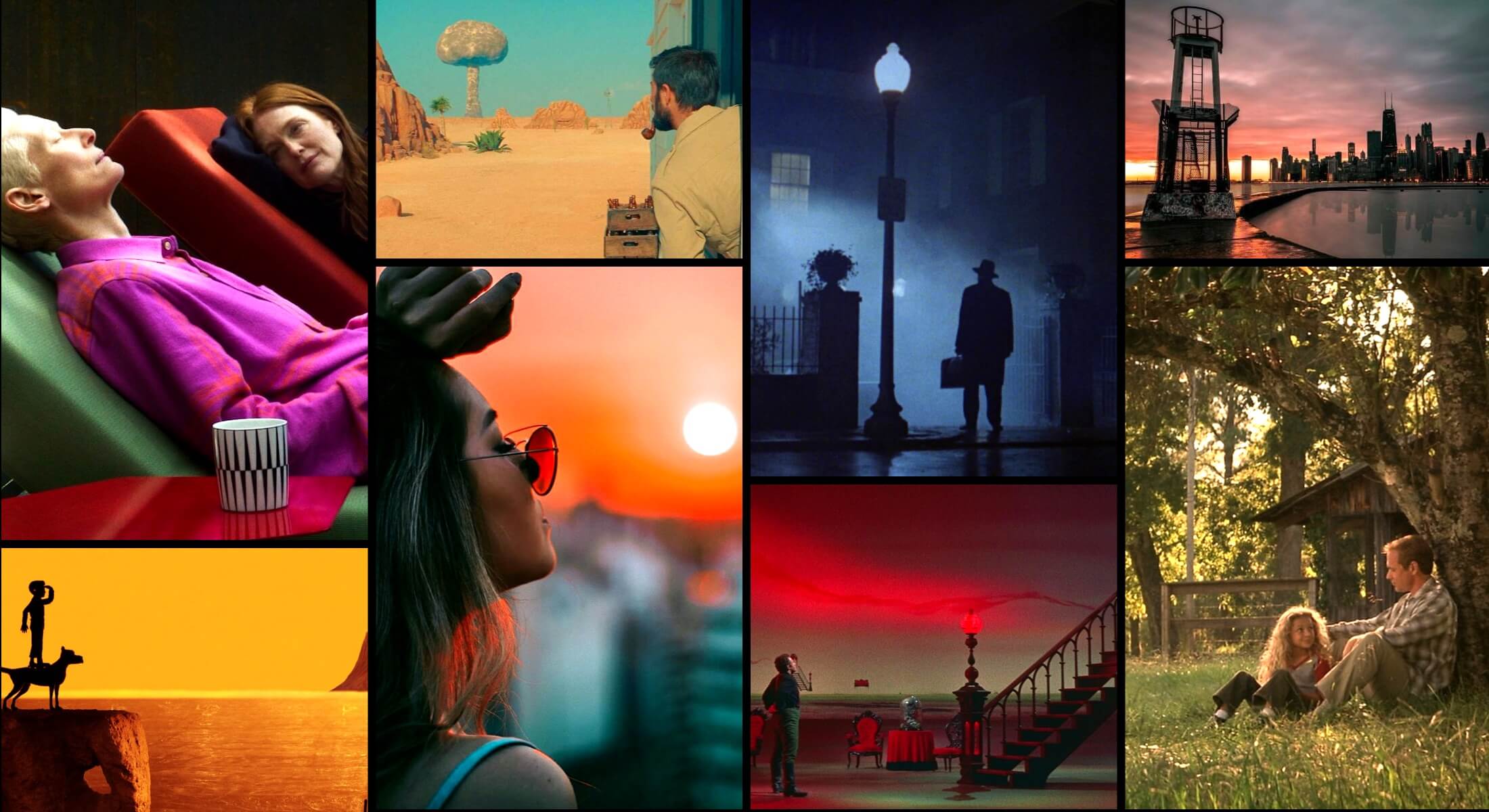
Non symmetrical balance examples
Asymmetrical balance examples
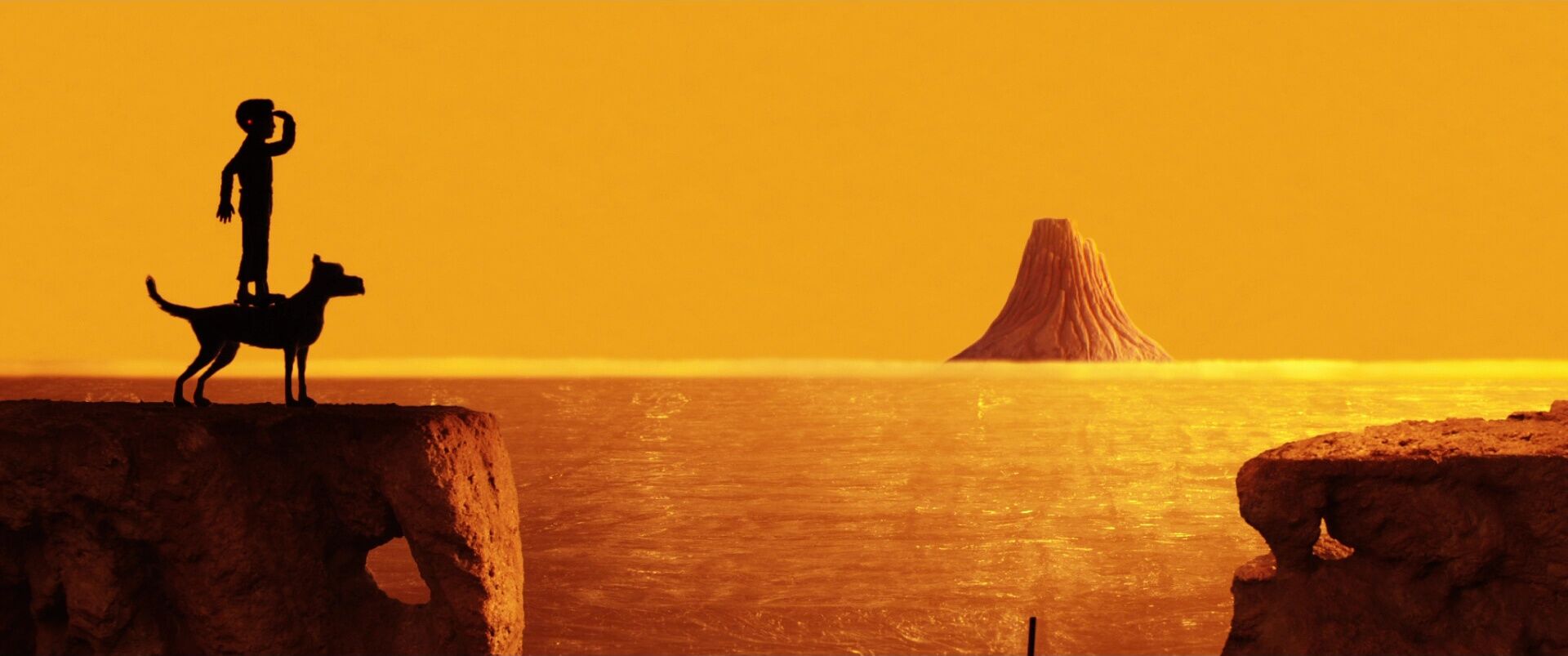
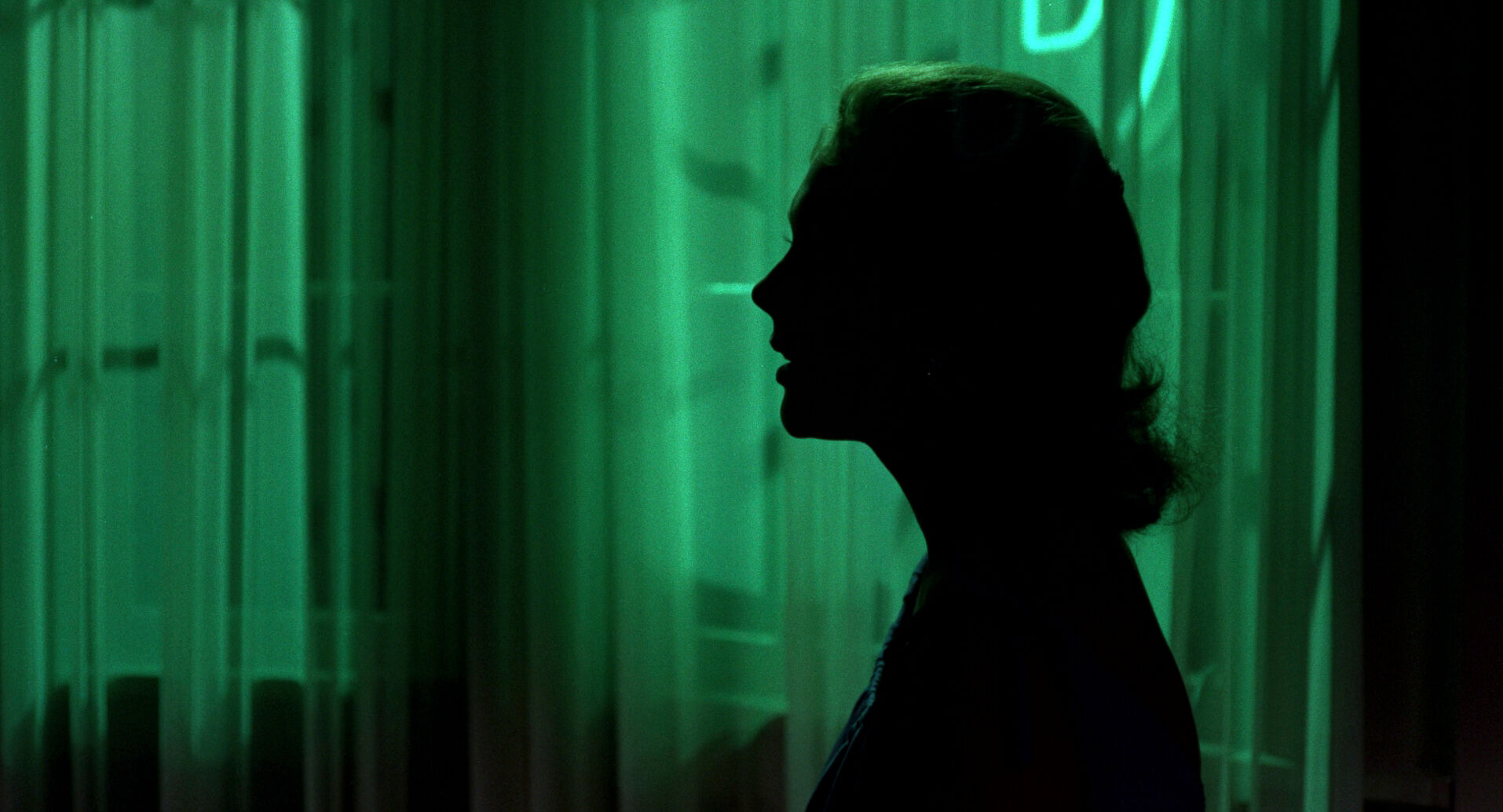
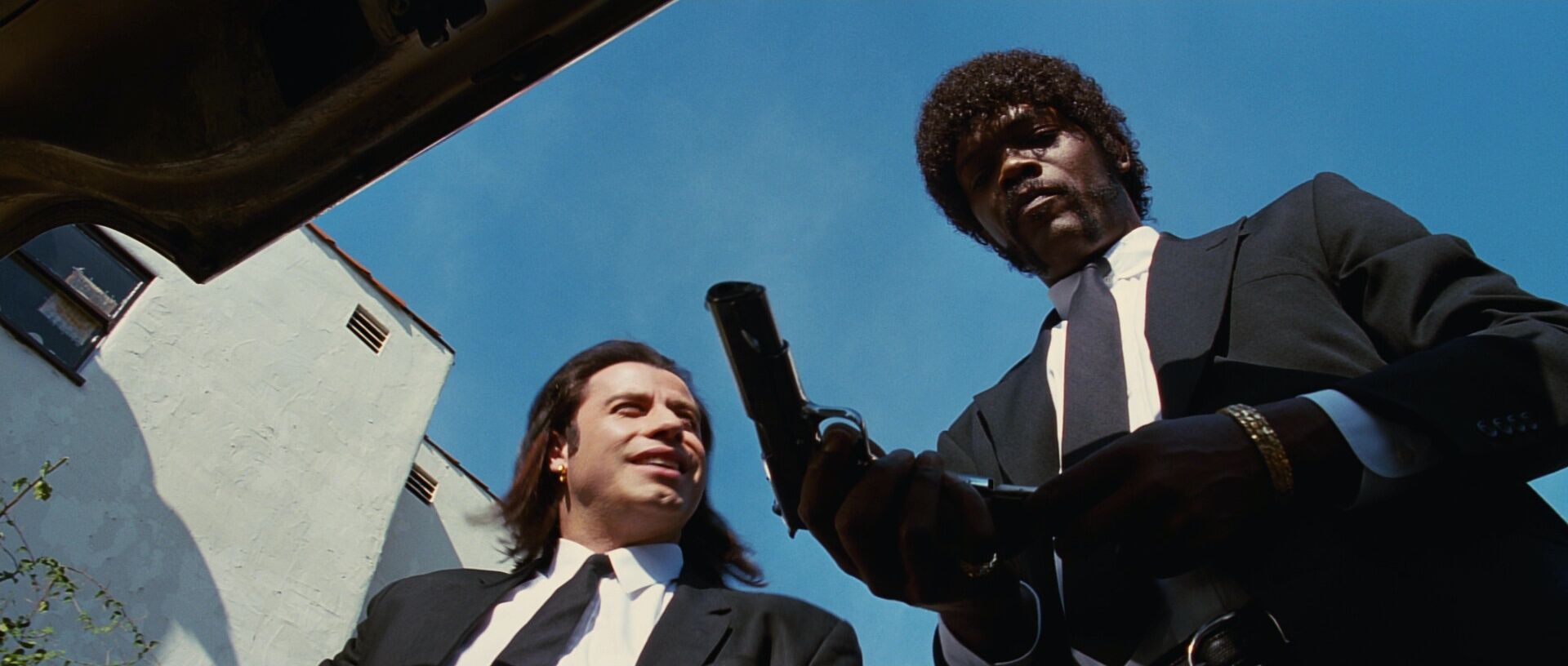
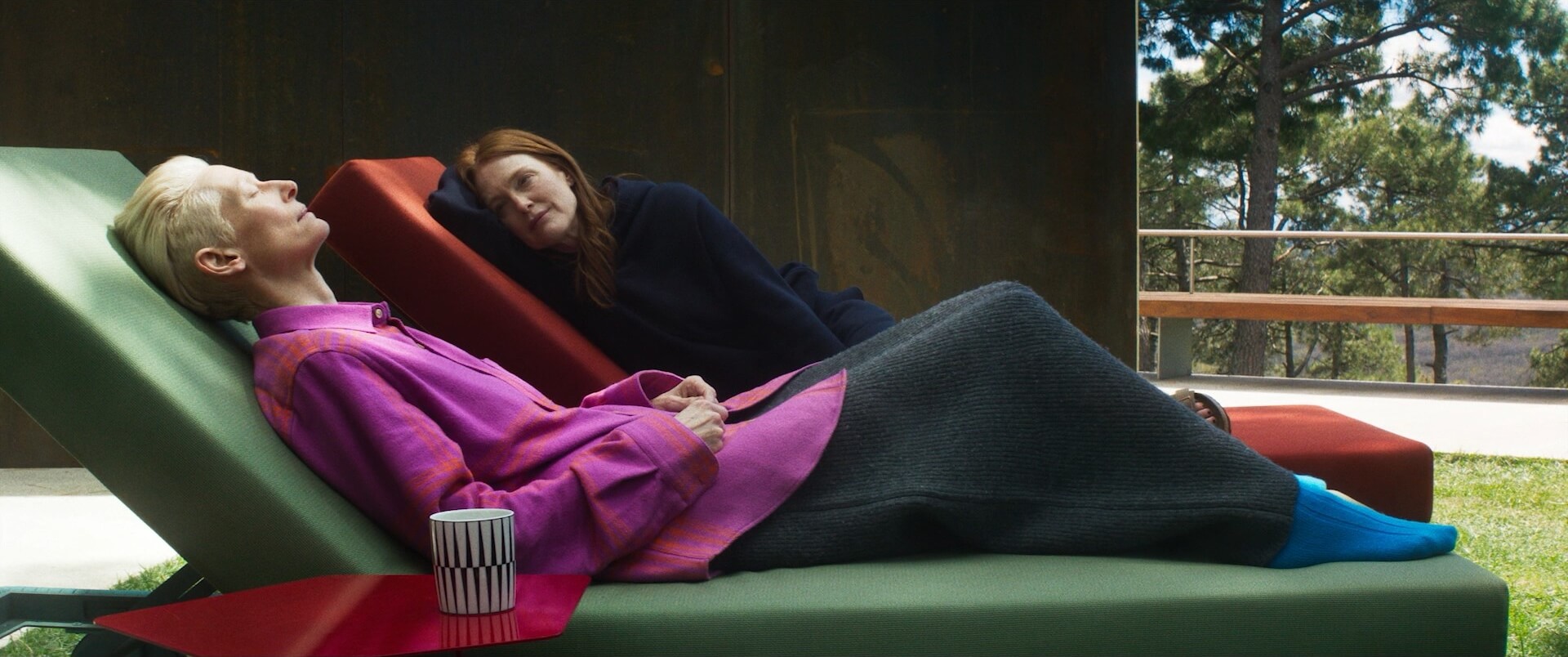
It’s helpful to see some examples of non-symmetrical compositions before exploring how they operate within visual storytelling. Browse this curated selection to get a sense of how these frames look across films.
Balance a shot
Create cool visuals
Convey tension
Show emotion
Uses
What does an asymmetrical shot do?
Asymmetrical shots may not be symmetrical, but they can still achieve balance, and often in more visually interesting ways than a perfectly symmetrical shot.
Create interesting compositions
Filmmakers use asymmetry to create unique and exciting visuals that don't exactly play by the rules in terms of balancing the frame.
Emphasize character moments
Sometimes you can balance positive and negative space with a character on one side and emptiness on the other especially pairing light with shadows.
Add tension
Putting things off-center in the frame can create a feeling of tension especially when using diagonals to create a balanced asymmetry.
Reveal relationship dynamics
Arranging a shot asymmetrically can imply dynamics between two characters in a scene depending on how they’re positioning relative to each other.
Balance in art
What is the difference between symmetrical and asymmetrical balance
Symmetrical balance in film would be a shot where both sides of the frame are identical, or mirrored. Meanwhile, in an asymmetrically balanced frame, things are off-center. It's a little misleading to say "balance" because that suggests equal weight on both sides. But that doesn't apply to visual composition — as long as we have something complementary on the other side, "balance" can be achieved.

Case Study
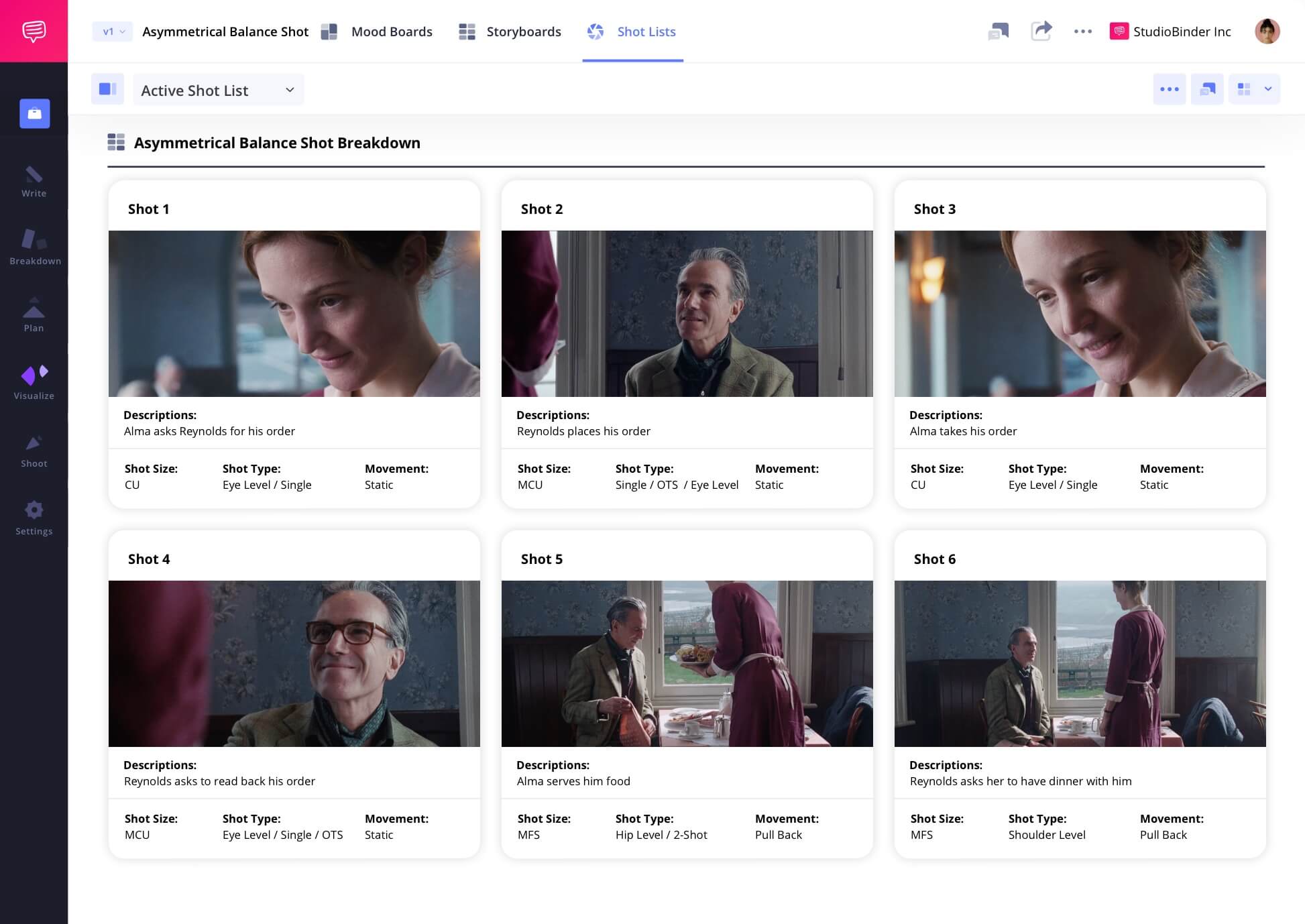
Shot listing an asymmetrically balanced shot
Asymmetrical balance is a fantastic way to visualize power dynamics between two characters. Even without dialogue, we can tell from the visuals which of the two has more power and this scene from Phantom Thread is a great example of that. As Reynolds meets Alma, she looms over him. She has made quite the impression on him and both with the blocking and composition, director Paul Thomas Anderson shows us that without words.
Click the shot list below to take a closer look at the entire scene.
Asymmetrical balance can be achieved in a variety of ways.
Unexpected combos
How can you create asymmetry with other techniques?
How to combine asymmetry
There are many techniques to help a filmmaker achieve an asymmetrical frame:
- Lighting: Focusing light or shadow on different parts of a frame can help create asymmetry.
- Color: Color can be a great way to draw the viewer’s eye to different parts of the frame.
- Camera movement: Using various camera shots, like tilts or crane shots, can create fluid visuals that emphasize asymmetry in a shot by making subjects closer or further away.
- Blocking: Arranging the actors in off-center ways in the frame will create an asymmetrical shot.
Frequently asked questions about asymmetrical balance
In a symmetrical composition, the two sides mirror each other. In an asymmetrical one, subjects in the picture are off-center.
Asymmetrical compositions can still look balanced if the filmmaker strategically distributes other things in the frame - like other subjects, color, or light.
In Alfred Hitchcock’s North by Northwest, a famous scene shows Cary Grant running from a plane. In this shot, Grant is off-center, taking up much of the right side of the frame, with the plane smaller in background on the left.
Symmetrical balance is when two sides of a frame mirror each other. This could be done on either the x or y axis and is typically achieved by placing the subject in the center of the frame with a consistent or parallel set design on either side of them.