home → Composition Techniques → Depth in Film
Frame depth definition
What is frame depth?
Film is a visual medium. Filmmakers tell their stories through a series of frames, creating different shot compositions to convey meaning, emotion, or interesting visuals. Movies are two-dimensional, but depth refers to the layers of a shot - foreground, middle ground, and background. Good shots arrange their layers to make the picture feel more three-dimensional.
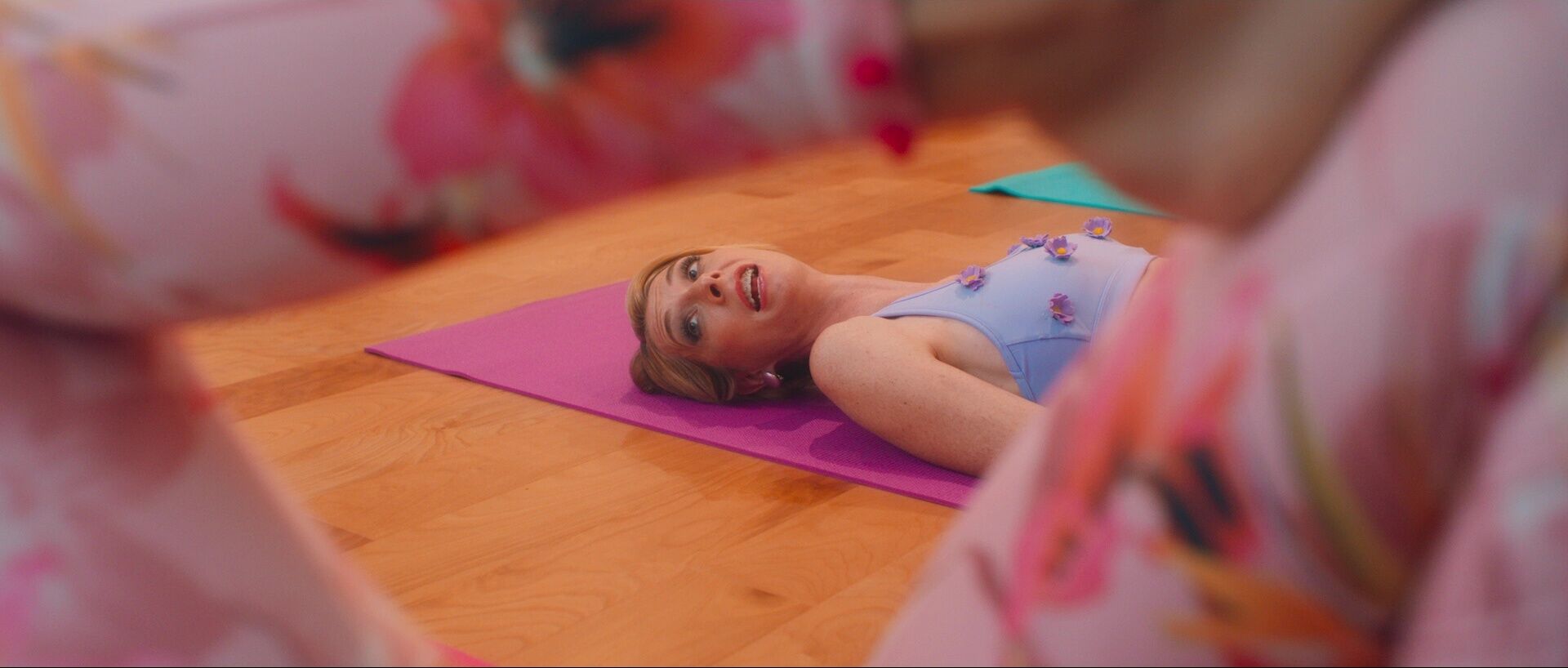
A shot’s depth of field refers to what is being focused on in the frame. This cues a viewer’s eye on where to look. For example, a shallow depth of field keeps the subject in focus, while the background or foreground is out of focus. This cues the viewer to keep their attention on the subject during the scene.
For an in-depth exploration of this technique, check out our full guide to film depth, complete with examples and breakdowns.
Depth of space in film examples
Depth cues in film examples
It’s helpful to see frames depicting depth of field before exploring how depth operates within visual storytelling. Browse this curated selection to get a sense of how depth works.
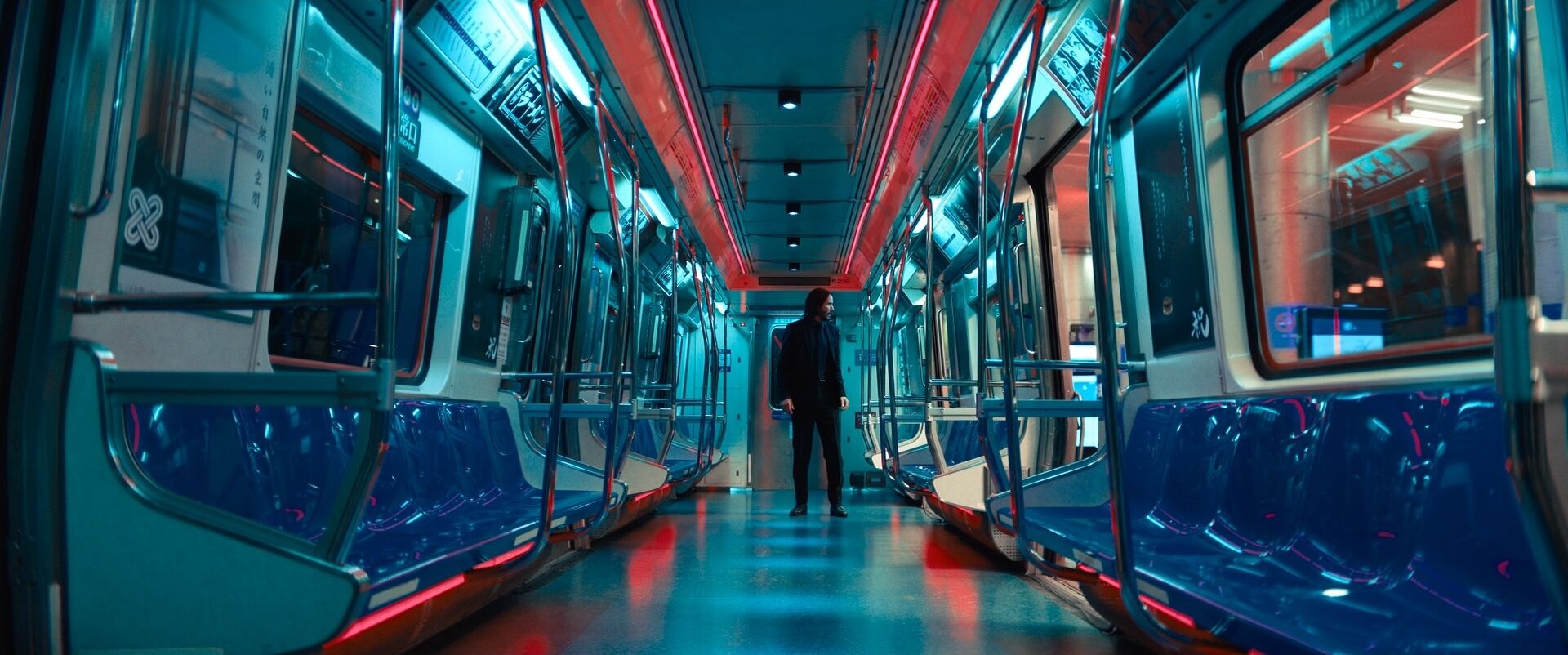
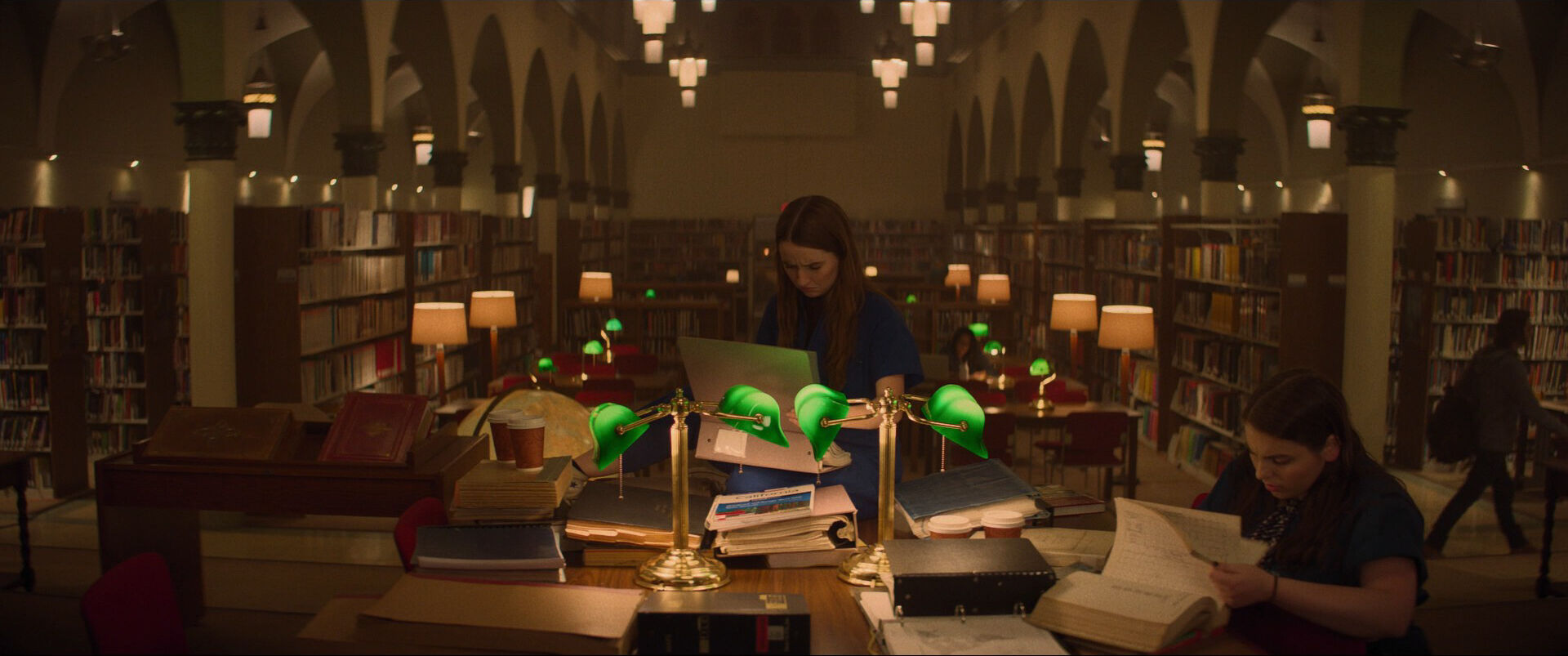
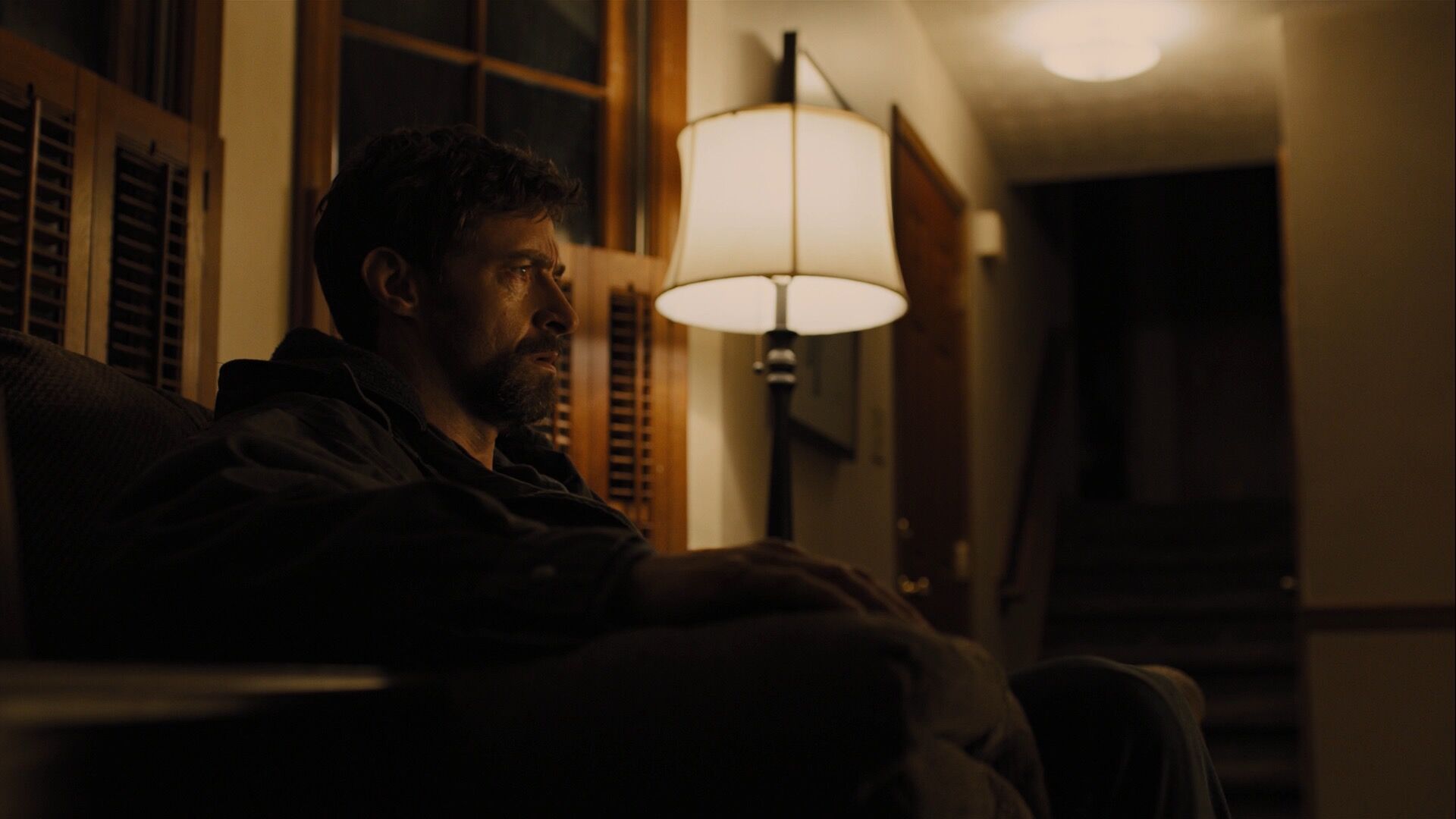
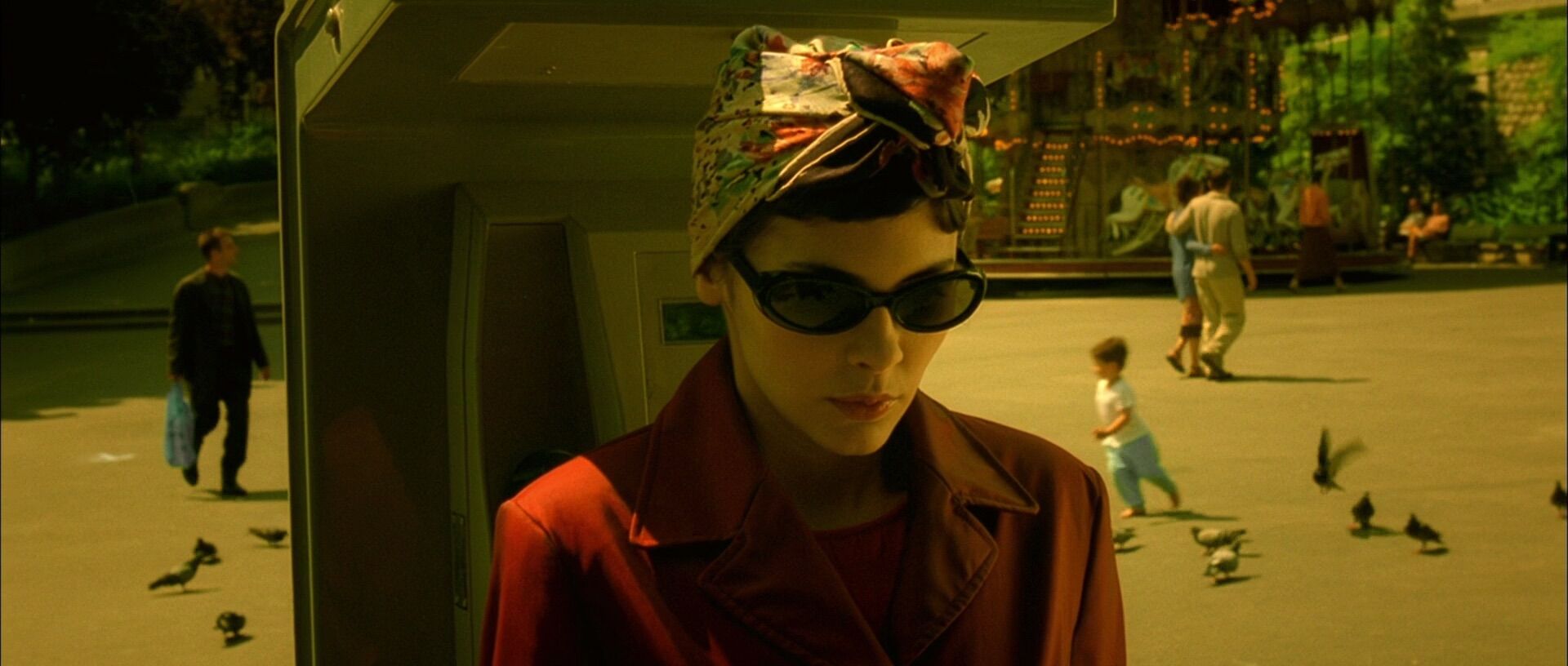
Deep depth of field
Shallow depth of field
Occlusion
Linear perspective
Uses
What does depth of field do?
By focusing on different depths of field, a filmmaker chooses where the viewer’s attention will go, and what part of the picture they are going to focus on, which impacts how they perceive the story.
Cues viewer’s eye
Choosing a depth of field helps direct a viewer where to look in the frame by keeping the entire scene and its space in full focus.
Make shots feel more real
Adding layers to your shot compositions can help make the visual experience feel more three-dimensional. It's a simple yet effective trick.
Create interesting visuals
Layered compositions create a more visually stimulating experience for the audience because it feels more like the real world and not just a flat image.
Evoke emotion or meaning
Cueing a viewer where to look using depth of field helps the audience understand character moments and emotions, or notice key story points.
Depth of space
Depth of field vs depth of space
Depth of field refers to what is sharp or focused on within the image. Meanwhile, depth of space refers to the various layers of the show, and how they are composed to make the frame seem more three-dimensional.

Case Study
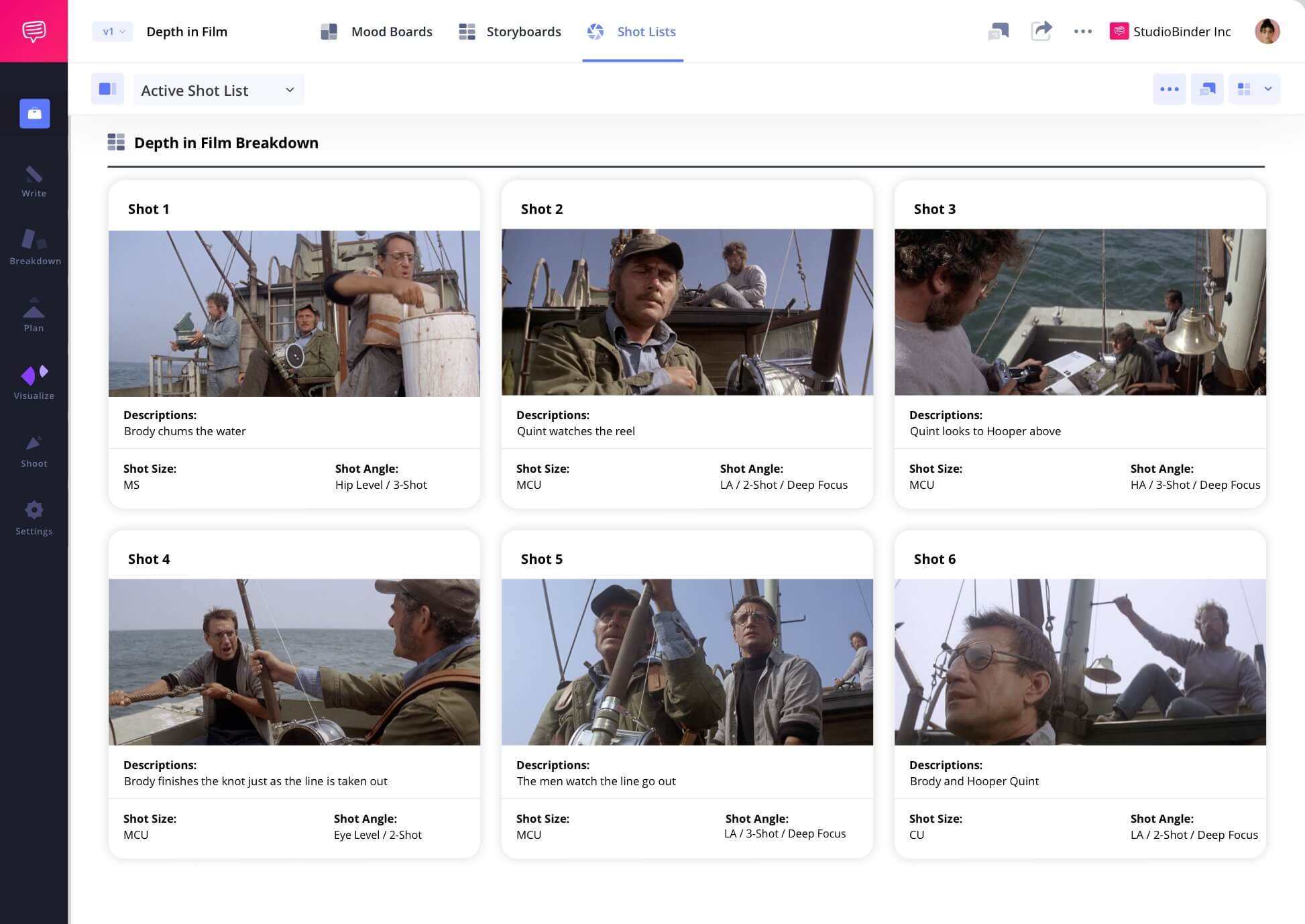
Shot listing depth in the frame
One of the many things Steven Spielberg is known for is his blocking and staging. Not only does he seem to find the most interesting ways to move the actors and the camera, he also simultaneously adds depth to the image and the character relationships. Take this scene from Jaws, where he makes sure to capture two or all three characters in the same shot to help build their bond on their journey. At the same time, this layered blocking creates a strong sense of depth in the image.
Click the shot list below to take a closer look at the entire scene.
Depth of field is important to consider when crafting your shot list, and achieving three-dimensionality can be achieved in conjunction with other film techniques such as lighting and camera moves.
Unexpected combos
How can you use depth of field with other camera techniques?
How to combine depth of field
Depth of field can be achieved using a variety of other filmmaking methods:
- Focus: This is a key element of depth of field. Creating a shallow depth of field means focusing on your subject, while blurring your background. A deep depth of field has a larger area of the frame in focus. Choosing focus involves adjusting the f-stop on your camera’s lens.
- Light and shadow: Light and shadow can be used to draw attention toward or away different aspects of the frame.
- Camera moves: Changing depth of field while moving the camera - whether that’s during a tracking shot or a crane shot - will change the viewer’s experience of the shot.
- Leading lines: Placing lines - such as stairs, fences, roads, or hallways - in different layers of the shot will affect how viewers experience the picture.
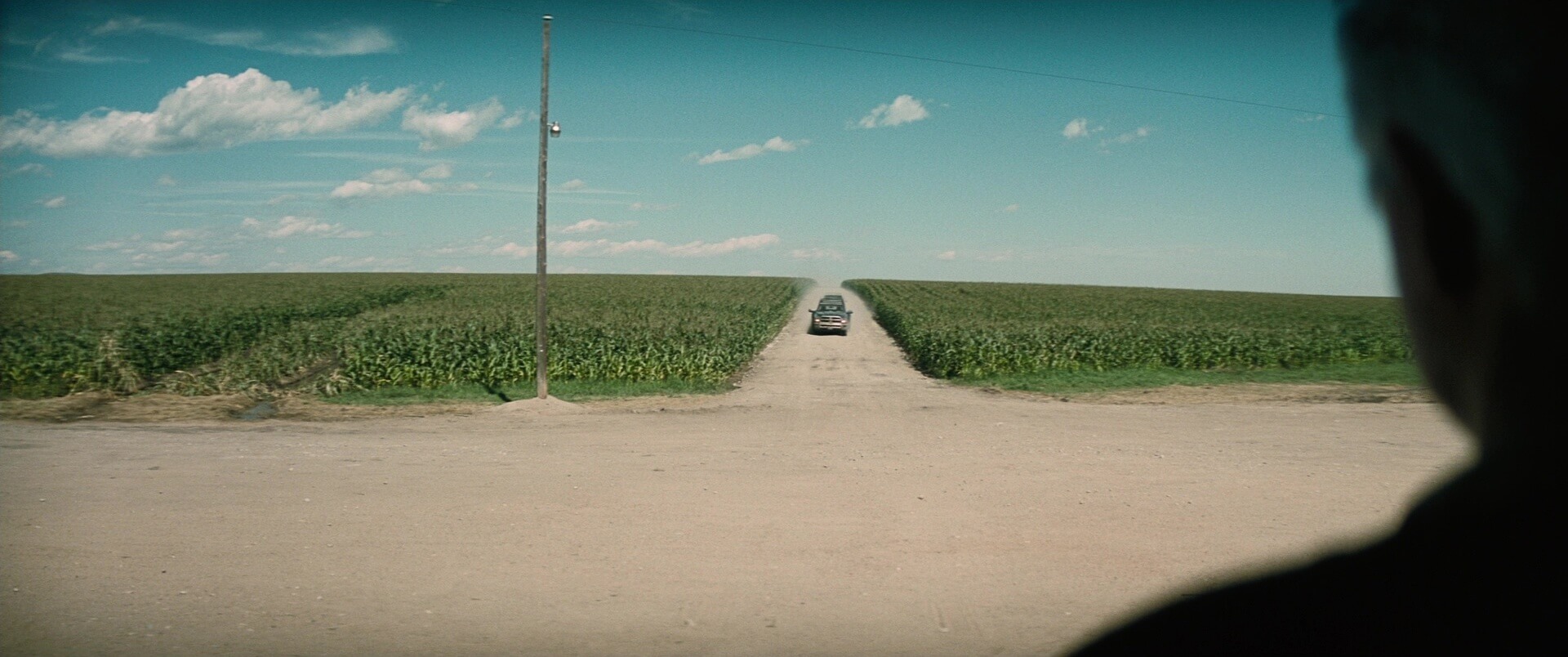
- Occlusion: Occlusion involves obstructing a distant object in the background with another object in the foreground. Filmmakers sometimes do this to create suspense.
Frequently asked questions about the depth of field
Depth of field refers to what area of the shot is in focus.
A shallow depth of field keeps the subject in focus, while the background or foreground is out of focus.
A deep depth of field keeps a larger portion of the frame in focus.
Controlling what is in focus tells the viewer where to look during the scene.