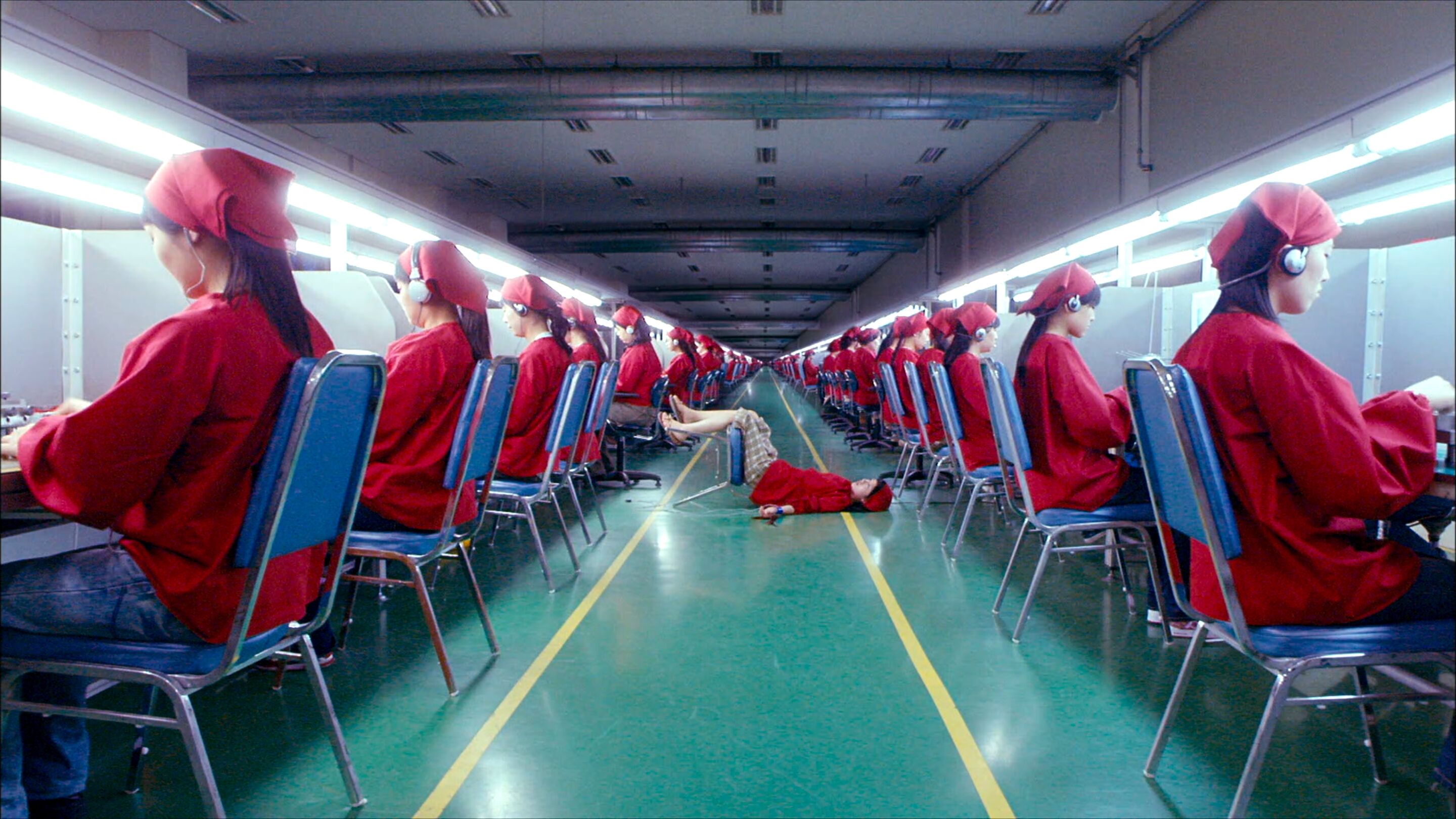
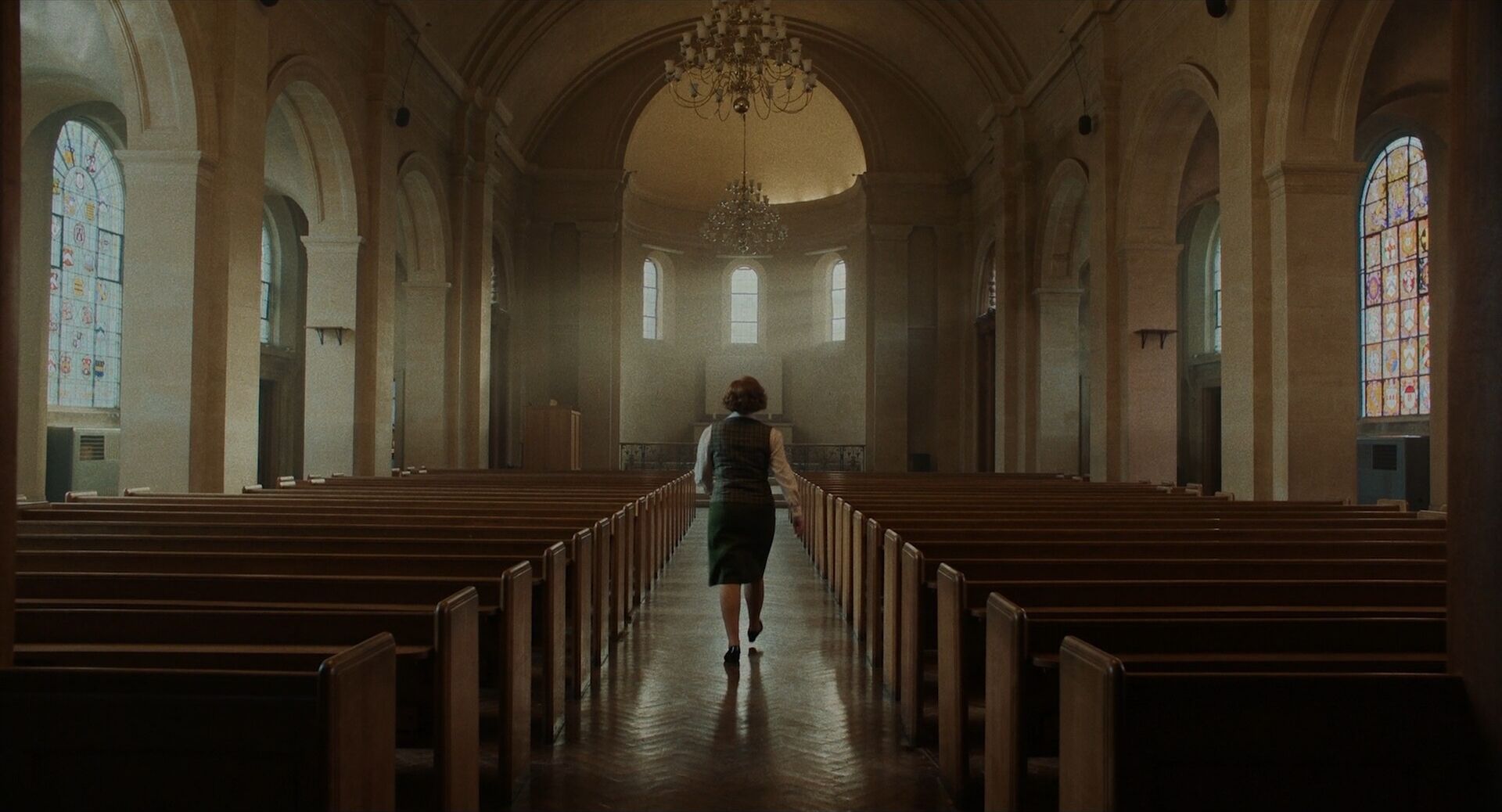
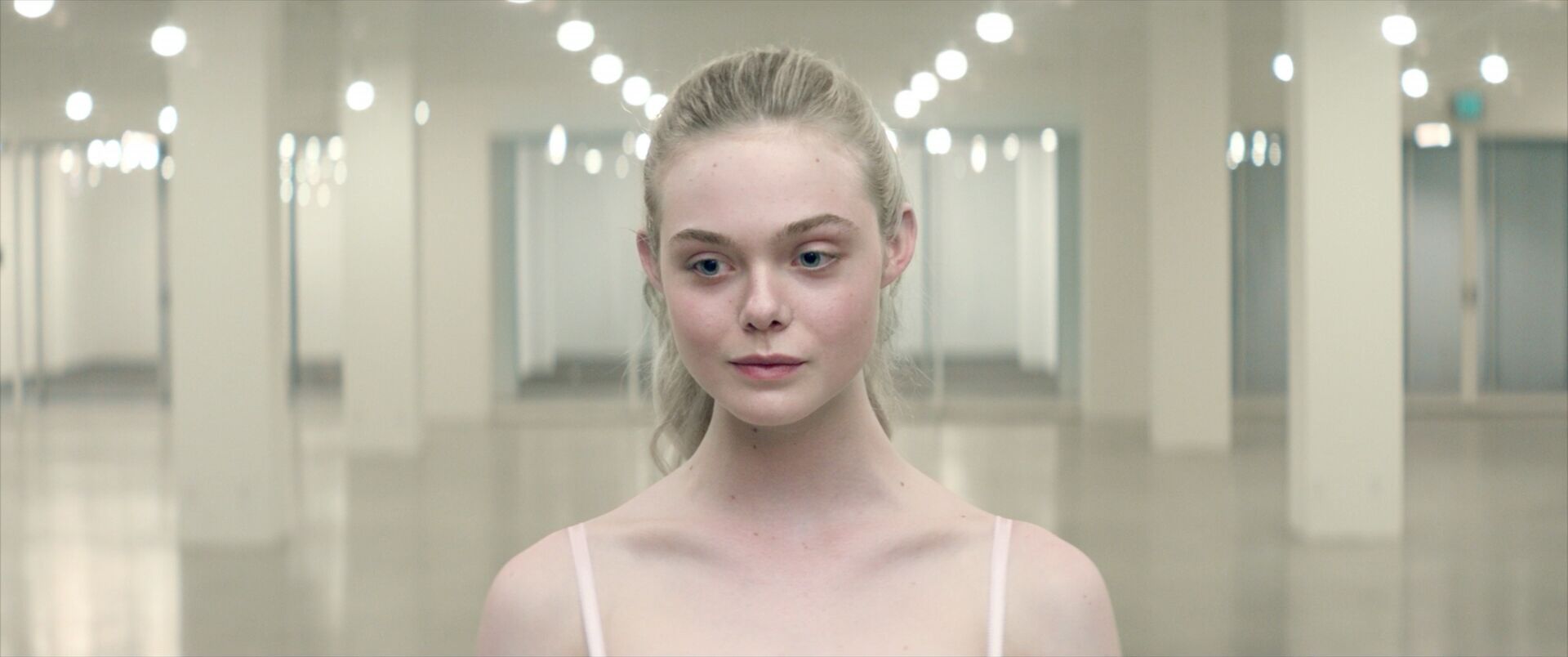
home → Composition Techniques → Symmetrical Balance
Symmetrical balance definition
What is symmetrical balance?
Filmmakers use shot lists to determine how each shot or frame in their story will look. When composing shots, filmmakers consider balance - how evenly or unevenly weight is distributed in the picture. Symmetrically balanced shots are pictures where the two sides perfectly mirror each other, with each side being perfectly balanced or even with the other. Filmmakers use different techniques - like lighting, color, and blocking - to achieve symmetrical shots.
For an in-depth exploration of this technique, check out our full guide to symmetrical shots, complete with examples and breakdowns.
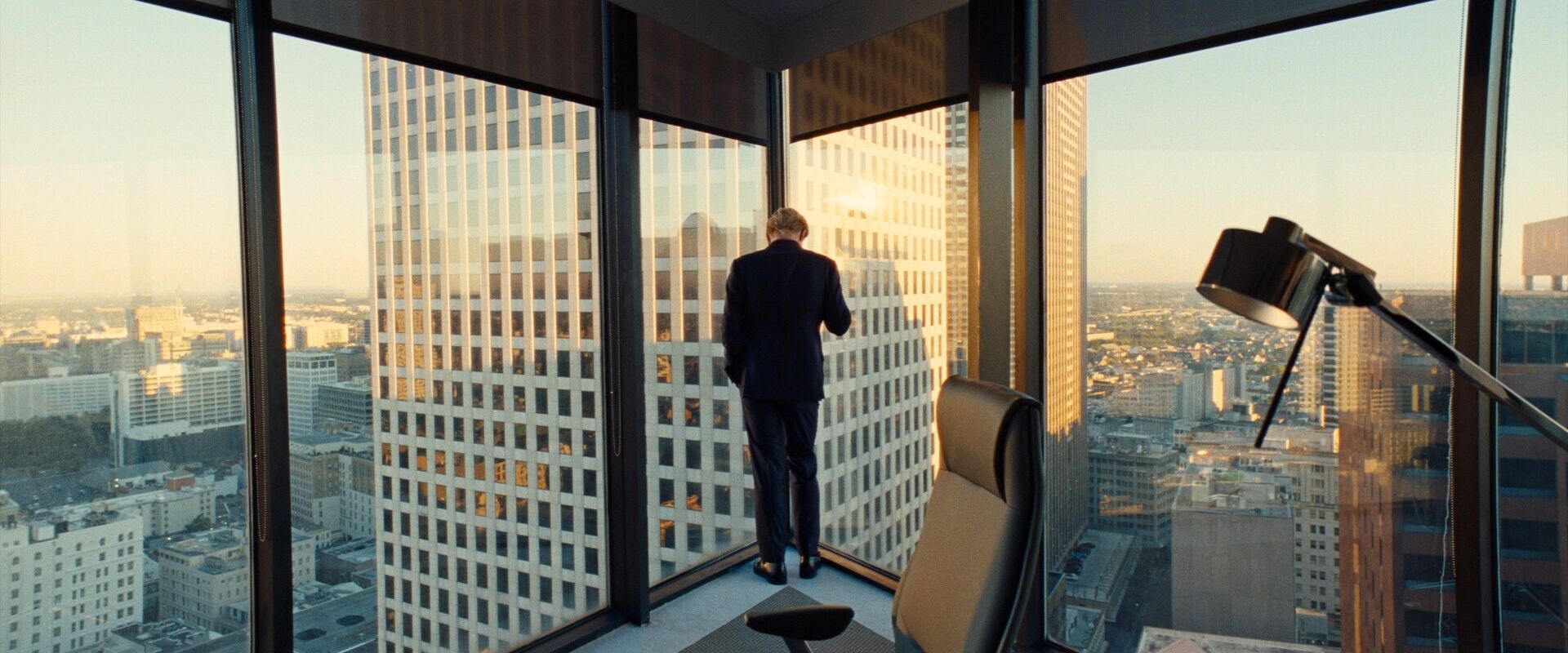
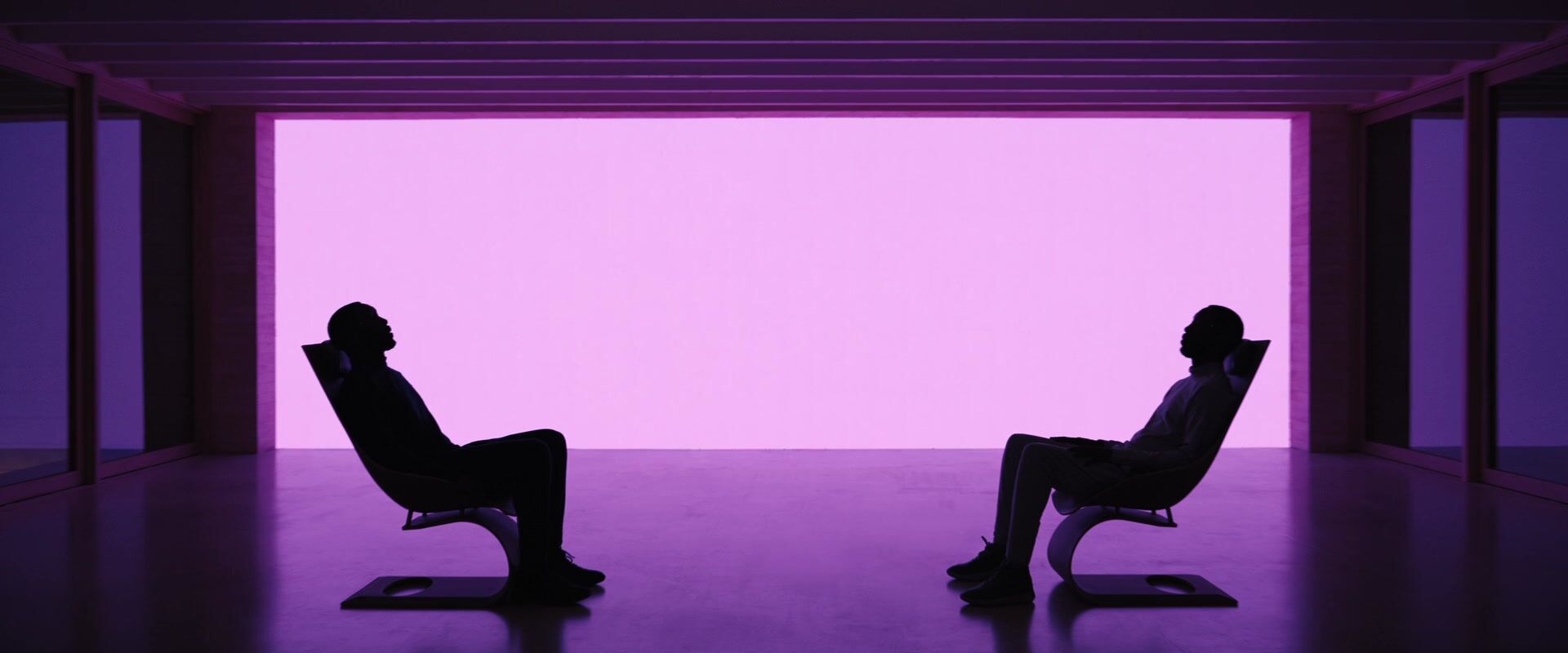
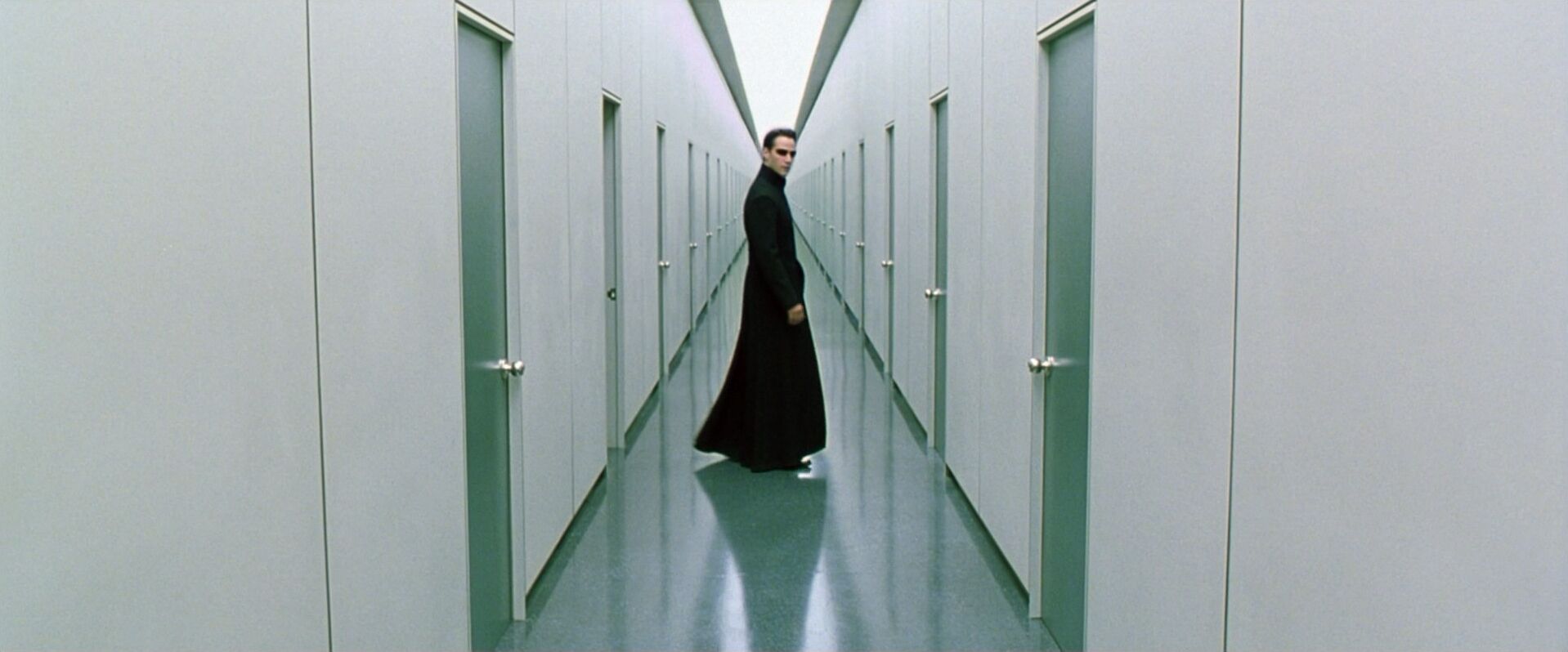
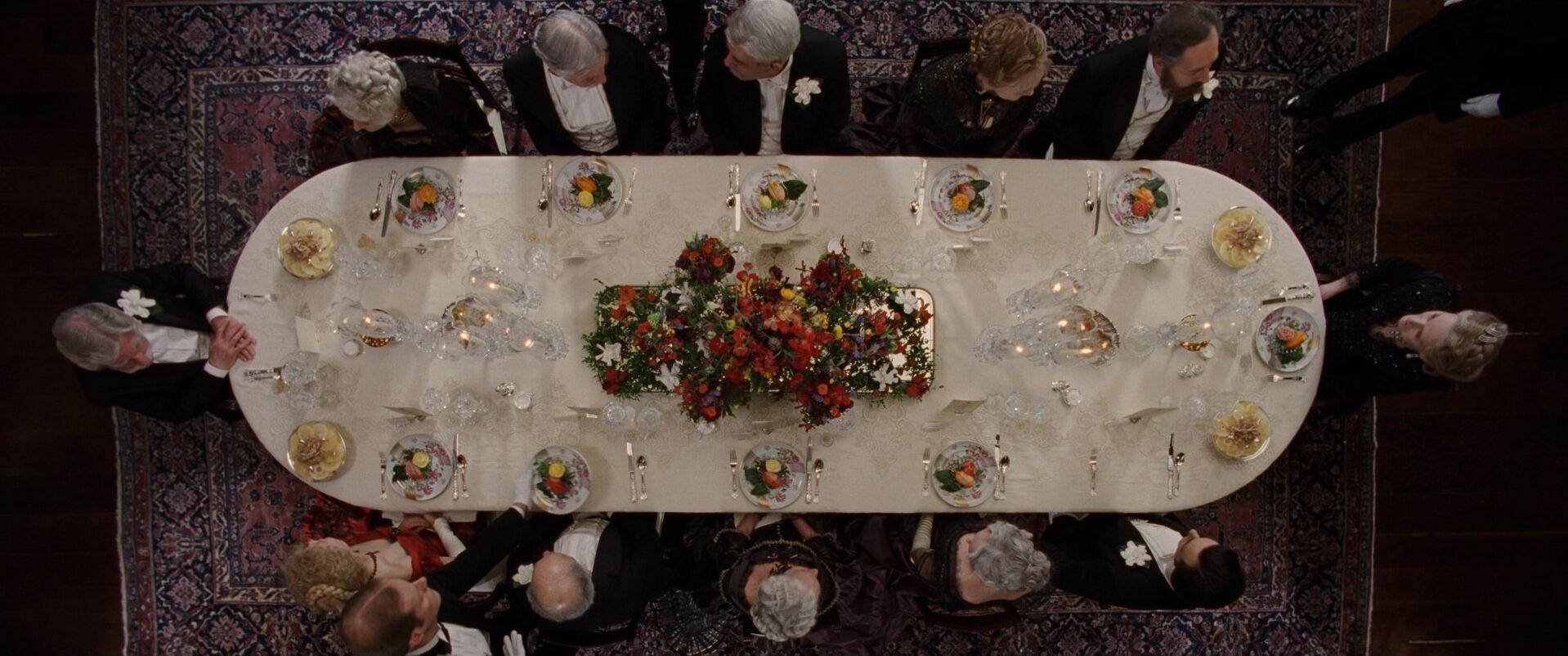
Symmetrical balance images
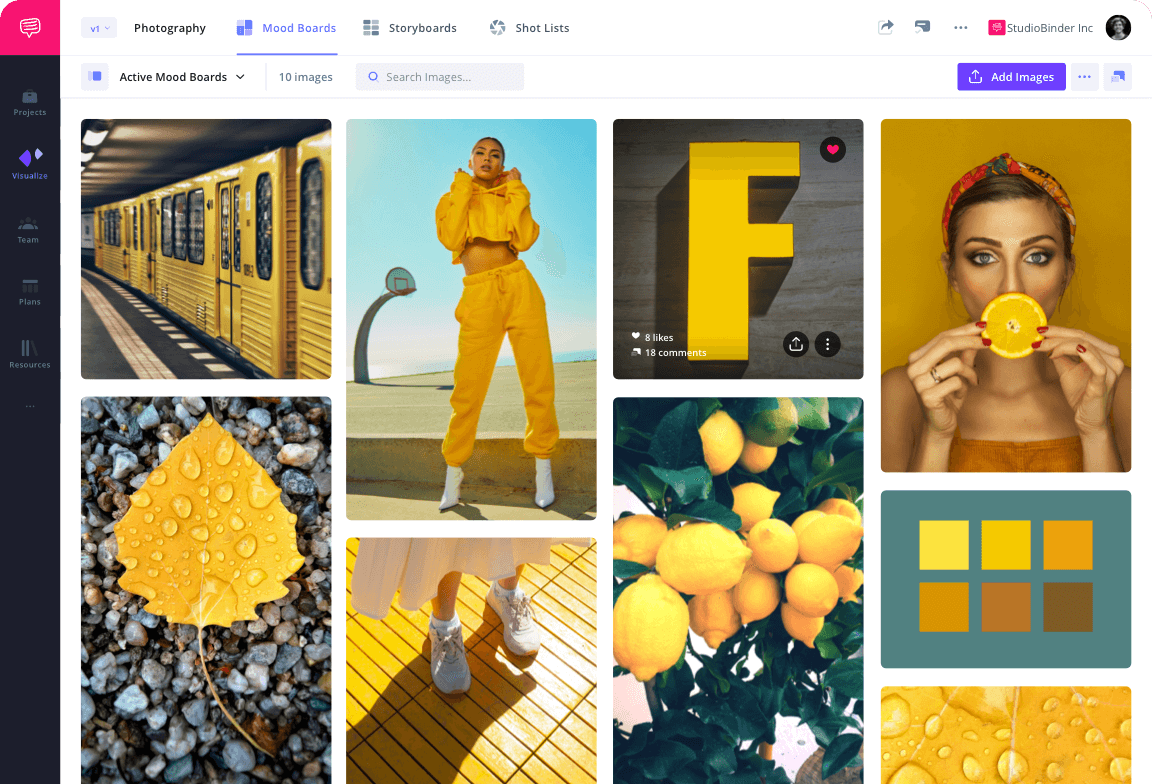
Symmetrical balance examples
It’s helpful to see symmetry in action before exploring how it can operate within visual storytelling. Browse this curated selection to get a sense of what symmetrical shots look like across films.
Achieve balance
Create cool visuals
Establish a focal point
Show order or structure
Uses
What does a symmetrical shot do?
Filmmakers use symmetrical shots for a variety of story reasons. In some cases, it clearly suggests a character in control, or the world around the character controlling them. There is a beauty to these symmetrically balanced shots, creating patterns and compositions that draw us straight in.
Create a sense of order
Shots with symmetry can feel ordered or clean, or even oppressive, which might be helpful for establishing a location or environment in the story.
Add visual interest
Symmetry is cool to look at! It is pleasing to the eye, which is one of the many reasons filmmakers might choose to make a shot symmetrical.
Direct a viewer’s eye
A frame with symmetry might have a key subject in the center of the frame, which will direct the viewer to keep their attention there.
Environment
Often, symmetrical shots speak more to the world around the characters than to the characters themselves, creating a visual relationship for us to decode.
Asymmetrical vs symmetrical balance
What is the difference between symmetrical and asymmetrical balance
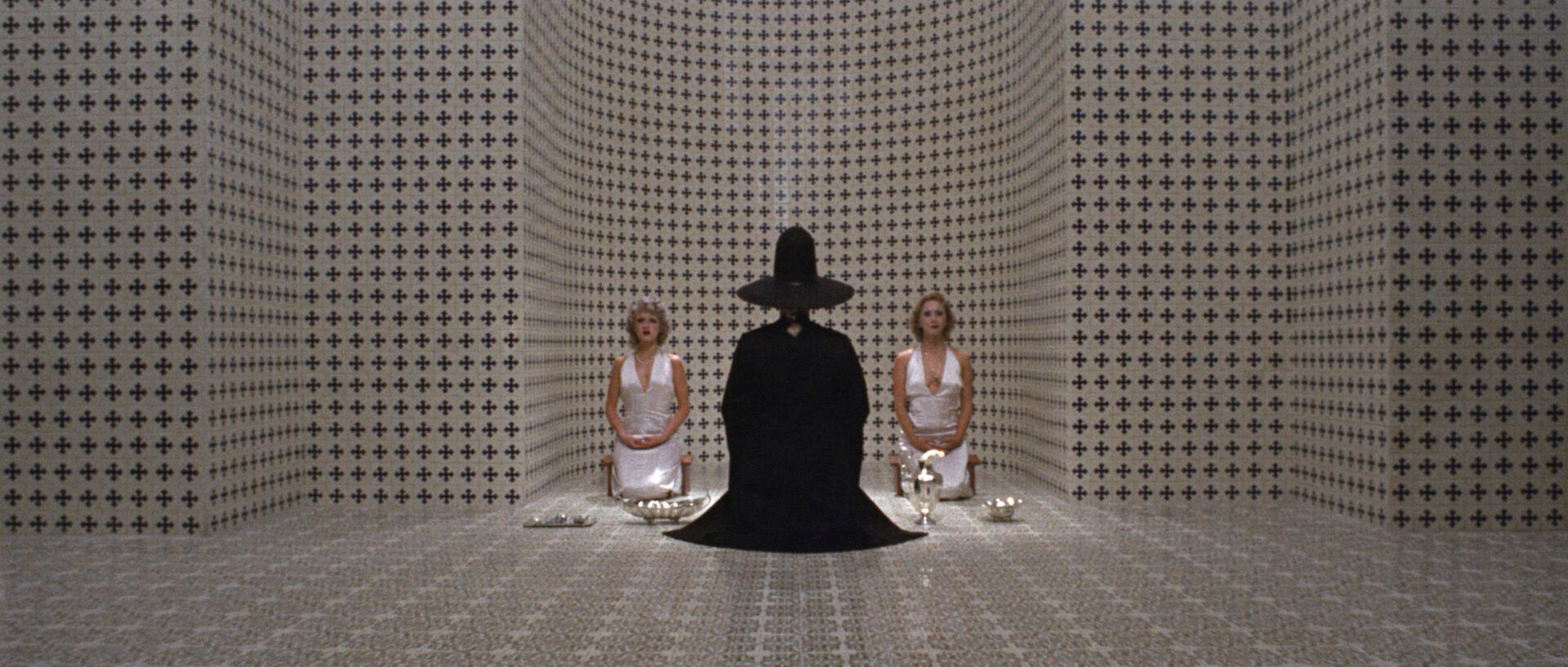
Symmetrical balance in film would be a shot where both sides of the frame are identical, or mirrored. Meanwhile, in an asymmetrically balanced frame, things are off-center.
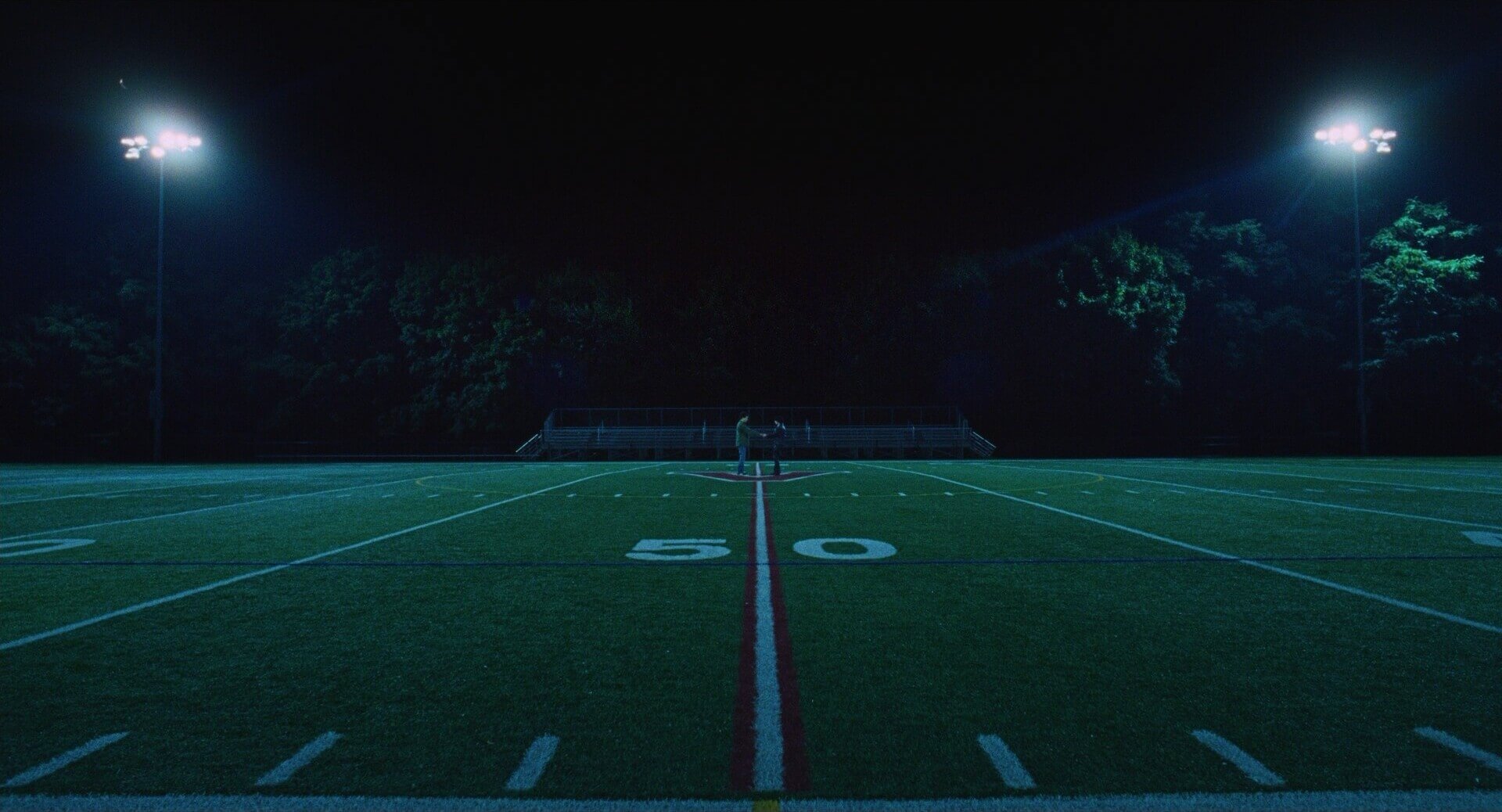

Case Study
Shot listing a symmetrical shot
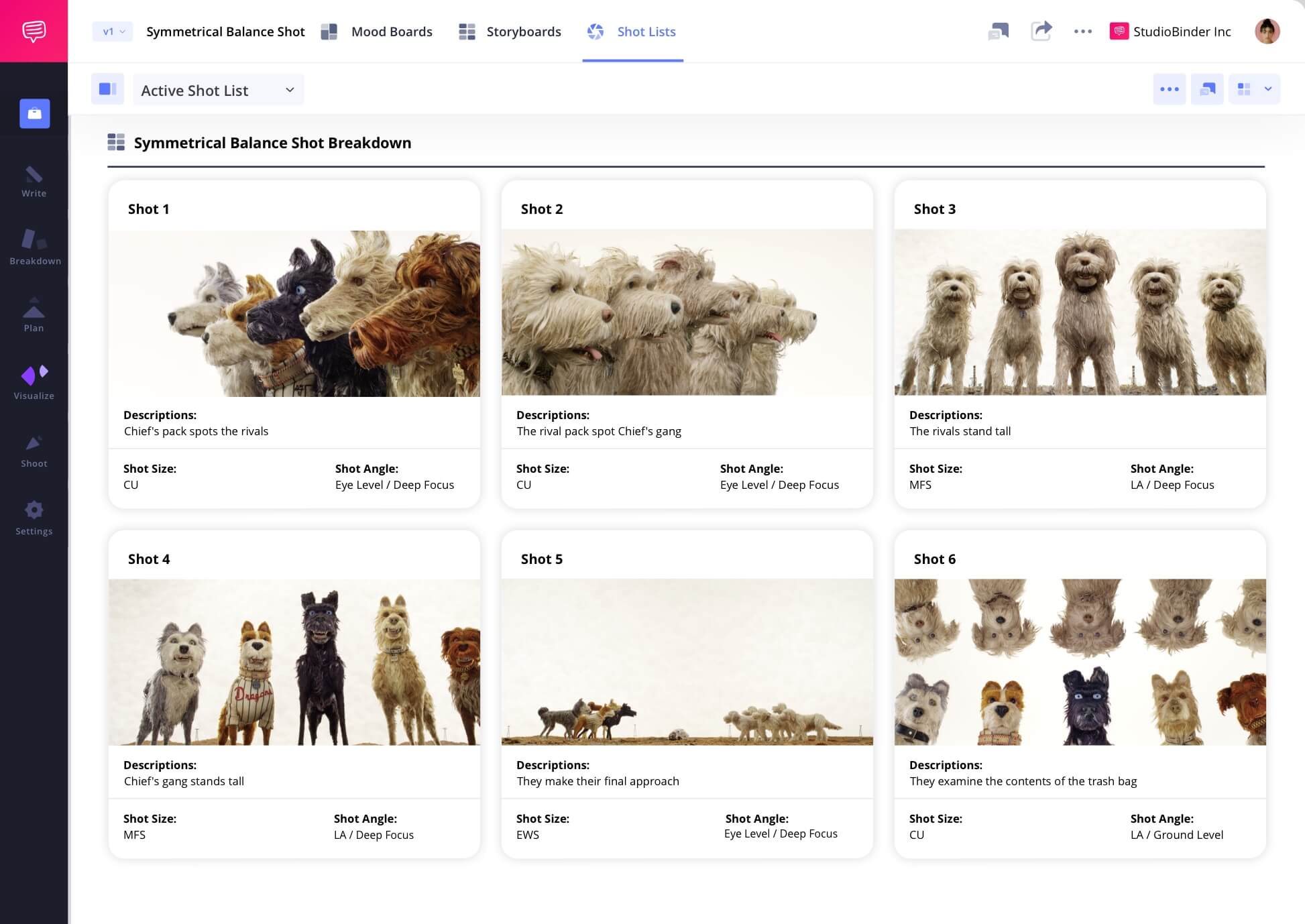
Many consider the master of symmetry in film to be director Wes Anderson. In a key scene from Isle of Dogs, two rival dog packs confront each other over an unclaimed bag of trash and the treasures within it. To amplify the tension and conflict, Anderson creates a series of symmetrical frames — both inside each frame and between consecutive frames.
Click the shot list below to take a closer look at the entire scene.
Symmetrical balance can be achieved in a variety of ways.
Unexpected combos
How can you use symmetry with other film techniques?
How to combine symmetrical shots
There are many techniques to help a filmmaker achieve a symmetrical frame:
- Lighting: Focusing light or shadow in equal measure on either side of a frame can help create symmetry.
- Color: Color can be evenly distributed throughout the picture to draw the viewer’s eye to different parts of the frame.
- Camera movement: Using various camera shots, like tilts or crane shots, can create fluid visuals that emphasize symmetry in a shot.
- Blocking: Arranging the actors parallel on either sides of the frame will create a symmetrical shot.
Frequently asked questions about symmetrical balance
Symmetrical balance is when visual elements are arranged on both sides of a picture equally. Each half mirrors the other.
Symmetrical balance in film would be a shot where both sides of the frame are identical, or mirrored.
In the opposite direction, with shots that are asymmetrical, things are uneven on either side but there is still balance between them. For example a short character on the left and a tall character on the right still provide a sense of balance despite the asymmetry.
The work of Wes Anderson has many examples of shots with perfect symmetry, where both sides of the frame are identical.