Conjunctions are a part of speech that helps sentences flow smoothly. It connects words, phrases, and clauses so ideas feel clear and complete instead of short and choppy. In this guide, we explain what a conjunction is in grammar, the main types of conjunctions, and clear examples you can use in your own writing.
What is a Conjunction in Grammar?
First, let’s define conjunction
Before we delve into the different conjunction types and examples, let's first understand the fundamental definition of a conjunction.
In grammar, a conjunction is one of the eight parts of speech in the English language. Its main job is to link parts of a sentence so ideas connect clearly.
What is a conjunction definition
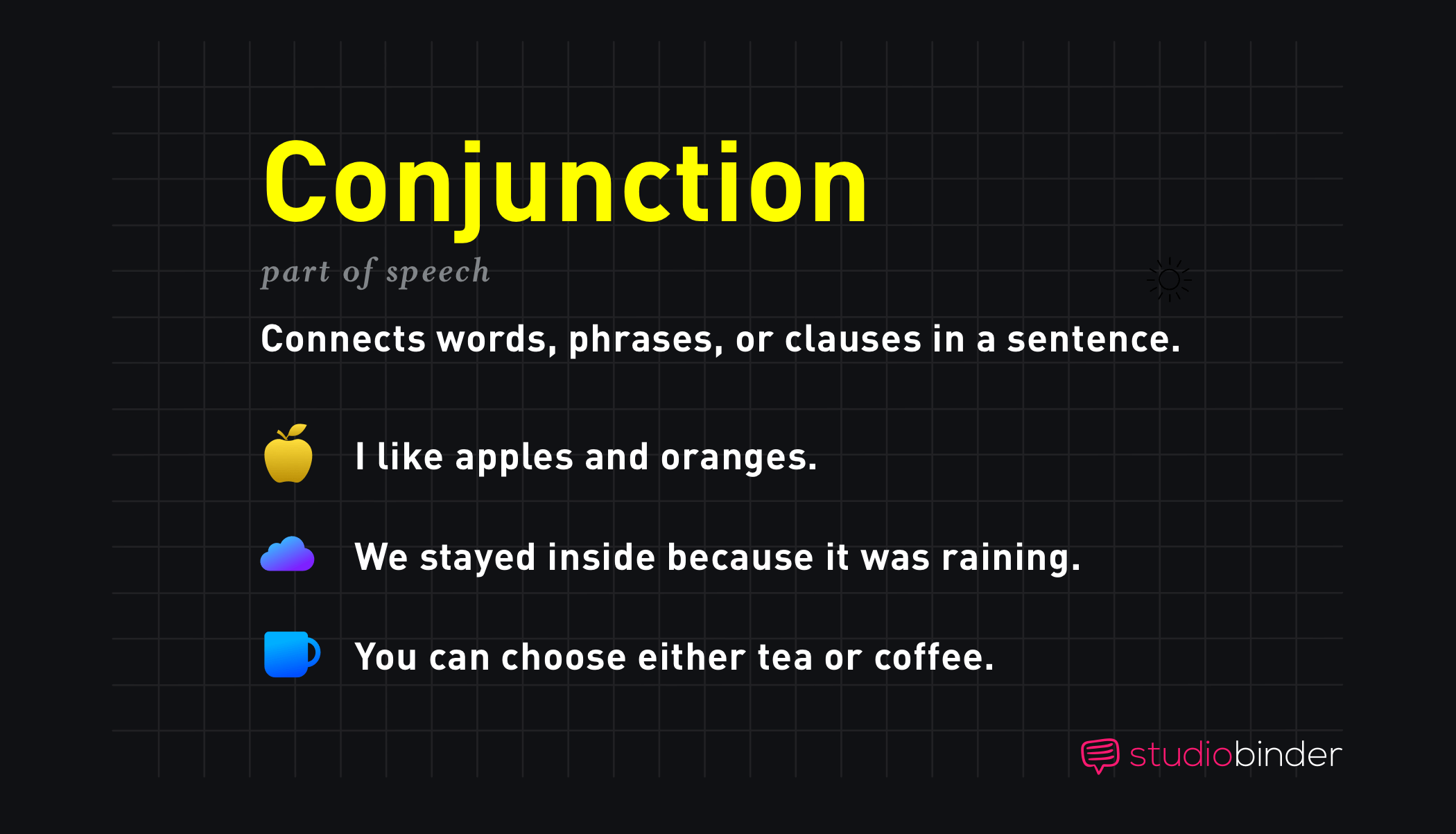
CONJUNCTION DEFINITION
What is a conjunction in grammar?
A conjunction is a part of speech in English grammar that connects words, phrases, or clauses. This answers common questions such as what is a conjunction, what a conjunction means, and what does the word conjunction mean.
A conjunction works like a bridge between ideas, helping sentences and paragraphs feel complete and easy to read. Conjunctions can join similar elements such as two nouns, two verbs, or two adjectives. They can also connect entire clauses to form longer sentences.
Examples of conjunctions in sentences:
- “I like apples and oranges.”
- “We stayed inside because it was raining.”
- “You can choose either tea or coffee.”
When it comes to using conjunctions, the following video does an excellent job at breaking it down even furhter.
The basics of conjunctions in grammar
Types of Conjunctions
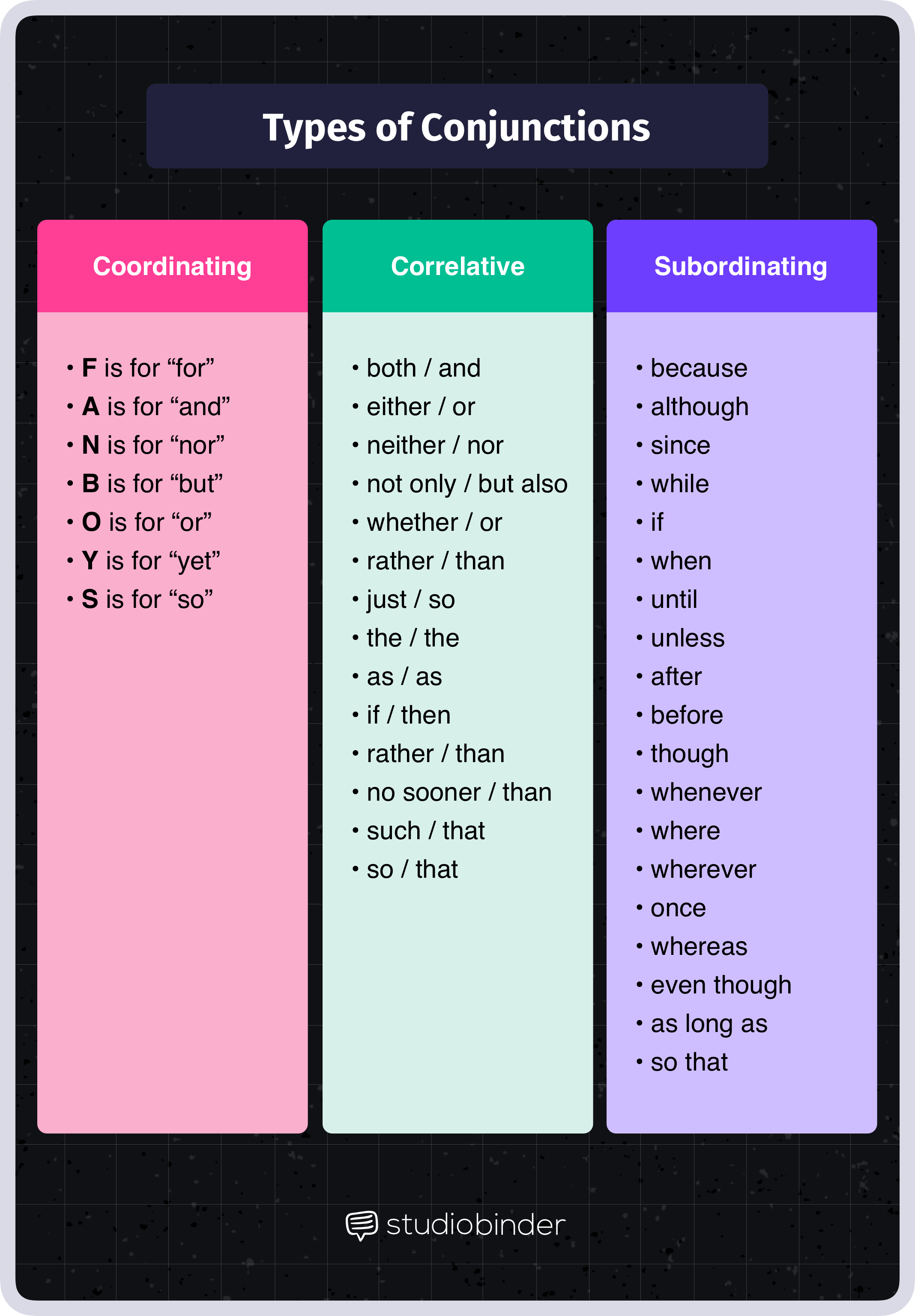
Types of Conjunctions
Conjunctions, which are crucial for connecting words, phrases, and clauses, can be categorized into three main types:
- Coordinating conjunctions
- Subordinating conjunctions
- Correlative conjunctions
Types of conjunctions used in grammar
Each type serves a specific purpose in sentence structure. Below are conjunctions in sentences examples that show how each type works in practice.
What is a conjunction - Types of Conjunctions with Examples
Each type serves a distinct purpose in sentence structure and plays a vital role in conveying meaning and coherence in written and spoken language.
Coordinating conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses that are grammatically equal. In other words, they connect two or more items of the same kind.
The seven coordinating conjunctions are often remembered using the acronym FANBOYS:
- For
- And
- Nor
- But
- Or
- Yet
- So
A sentence with a coordinating conjunction would be: “I wanted to go to the park, but it was raining.”
Subordinating conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to link a subordinate (or dependent clause) to a main clause (or independent clause), creating a complex sentence.
Examples include words like because, although, when, while, if, and since.
For instance, "Although it was raining, we decided to go out."
Correlative conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of conjunctions that work together to coordinate words or phrases.
These pairs include either/or, neither/nor, both/and, not only/but also, whether/or.
For example, in the sentence "Either you finish your homework, or you don't get to play video games," the pair 'either/or' is a correlative conjunction setting up a choice between two alternatives.
When to use each type of conjunction:
Conjunction Type | Sentence Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
Coordinating | Compound sentence | I stayed home, and I watched a movie. |
Subordinating | Complex sentence | I stayed home because it was raining. |
Correlative | Compound or complex | Either we leave now or we miss the train. |
Conjunction-related resources
Examples of Conjunction
What are some conjunction examples?
Conjunctions are crucial for constructing sentences. Knowing how to use them correctly can elevate your writing so that it flows smoothly and captivates your readers. Remember, reading is an experience designed by the writer so you have full control to make it an enjoyable journey or not.
What is a conjunction - With and without conjunction usage
Use Conjunctions to Improve Flow
If you're not using conjunctions, writing can sound repetitive. By connecting ideas, phrases, and clauses, conjunctions can help your writing sound more natural and less disjointed.
As The Editor’s Manual explains, “conjunctions link words, phrases, clauses, and sentences, and show a logical relation between them.”
According to the Chicago Manual of Style, as many as 10% of sentences in polished, professional writing begin with conjunctions such as and, but, or so. This shows that conjunctions are not only grammatically correct, but also commonly used to improve sentence flow and emphasis.
Examples:
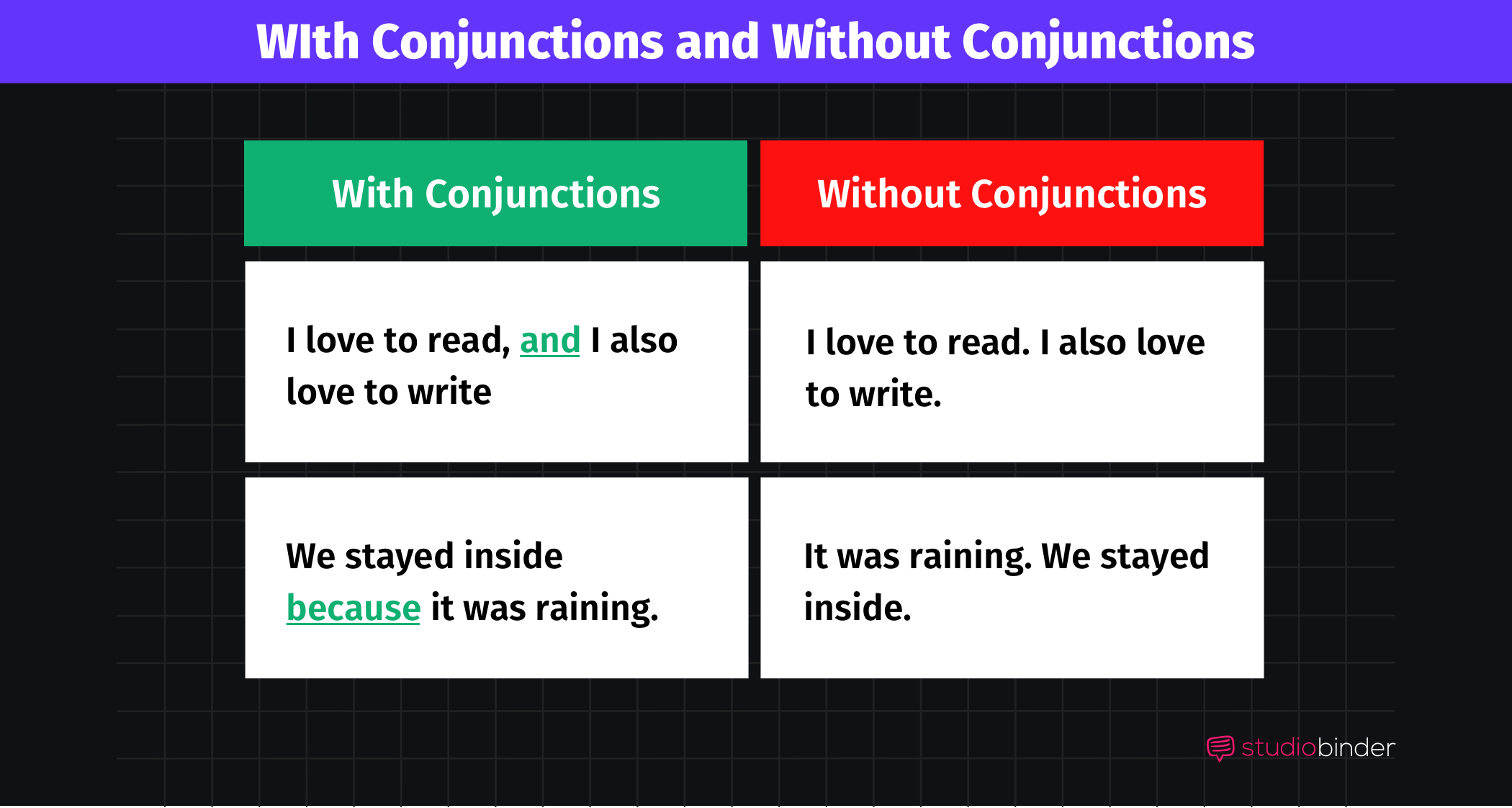
- Without conjunction: "I love to read. I also love to write."
- With conjunction: "I love to read, and I also love to write."
Avoid Overusing Conjunctions
While conjunctions are essential, it's crucial to avoid overusing them, as this can make your sentences long and confusing. It's better to keep your sentences simple and clear.
Example:
- Without conjunction: "I went to the store, and I bought apples, and I also got some oranges, and I paid with cash."
- With conjunction: "I went to the store. I bought apples and oranges and paid with cash."
Choose the Correct Type of Conjunction
When you're ready to pick a conjunction to use in your sentences, just remember:
- Use coordinating conjunctions to connect equal ideas
- Use subordinating conjunctions to link dependent and independent clauses
- Use correlative conjunctions to show pairs or choices
Examples:
- Coordinating: "I love apples and oranges."
- Subordinating: "We played outside until it got dark."
- Correlative: "Either you clean your room, or you can't go to the party."
Conjunctions do more than connect ideas. They also show how ideas relate to each other such as the examples shown below:
Relationship Shown | Common Conjunctions | Example |
|---|---|---|
Addition | and, also | I like apples and oranges |
Contrast | but, although | I wanted to go, but it was raining. |
Cause and effect | because, so | We stayed inside because it was cold. |
Choice | or, either/or | You can call me or text me. |
Time | when, while, after | Call me when you arrive. |
Condition | if, unless | If it rains, we will stay inside. |
Conjunctions play a crucial role in the English language. They help create connections and coherence within our sentences, making our writing flow smoothly. By following these guidelines, you'll make sure your writing is clear, engaging, and free from grammatical errors.
What is a conjunction and key examples to learn from
Related Sentence Types
Common Conjunction Mistakes
Common conjunction mistakes
Even though conjunctions are simple, they are often misused. As the grammar expert Professor Scott Mendoza explains, “they connect ideas, control flow, and help readers follow your meaning.” When used incorrectly, these small words can distort logic or leave your message unclear.
Here are a few common mistakes to avoid.
Comma Splices
A comma splice happens when two independent clauses are joined with only a comma.
- Incorrect: “I wanted to leave, I was tired.”
- Correct: “I wanted to leave, because I was tired.”
Starting Too Many Sentences With And or But
Starting sentences with and or but is not always wrong, but overusing them can weaken your writing.
Research on student writing shows how frequently conjunctions appear in real sentences. In one academic study, writers used an average of 23.49 conjunctions per essay, with additive conjunctions like and and but appearing most often. This high frequency helps explain why conjunction mistakes are so common.
Grammar related resources
Parts of Speech
Conjunctions vs other parts of speech
Conjunctions are sometimes confused with other parts of speech or subject in grammar, especially prepositions and adverbs.
- Conjunctions connect words or clauses
- Prepositions show relationships between a noun and another word
- Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs
Understanding these differences helps avoid grammar errors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Conjunction FAQs
A conjunction is a part of speech that connects words, phrases, or clauses to show relationships between ideas.
Below is a simple list of common conjunction words used in English writing which you can also use alongside other parts of speech or synonyms:
- Coordinating: and, but, or, so, yet
- Subordinating: because, although, since, while, if
- Correlative: either/or, neither/nor, both/and
Here is a list of 12 conjunctions:
- For
- And
- Nor
- But
- Or
- Yet
- So
- Although
- Because
- Since
- While
- Not only
An example of using a conjunction in a sentence would be: “She wanted to leave, but she stayed.”
Conjunctions help writing sound natural and organized by linking ideas logically. Without conjunctions, sentences would limited to simple statements. And while a simple, direct sentence is sometimes the most effective, a more complex sentence using conjunctions is often preferred. Conjunctions give writers the ability to create more complex and interesting sentences. They can combine ideas, create juxtapositions, add a sense of rhythm and so much more.
Up Next
What is a complex sentence structure?
Think of writing like architecture. The good writers understand the "design" element of the medium, and they also know when to make that design simple, complex, or something in between. At the most fundamental level, this design is achieved with sentence structure. Let's dive into conjunctions in our upcoming article on complex sentence structure.
